Prostate cancer survivorship: a new way forward
 Over 2 million people in England have a diagnosis of cancer. This is such a large problem, the Department of Health is spending £750 million on improving earlier diagnosis and prevention of cancer, yet at the same time, £20 billion of efficiency savings must be made. One arm of post-cancer care is survivorship. Survivorship care was initially developed in the USA 20 years ago, starting with breast cancer patients. Prostate cancer survivorship care has been lagging far behind.
Over 2 million people in England have a diagnosis of cancer. This is such a large problem, the Department of Health is spending £750 million on improving earlier diagnosis and prevention of cancer, yet at the same time, £20 billion of efficiency savings must be made. One arm of post-cancer care is survivorship. Survivorship care was initially developed in the USA 20 years ago, starting with breast cancer patients. Prostate cancer survivorship care has been lagging far behind.
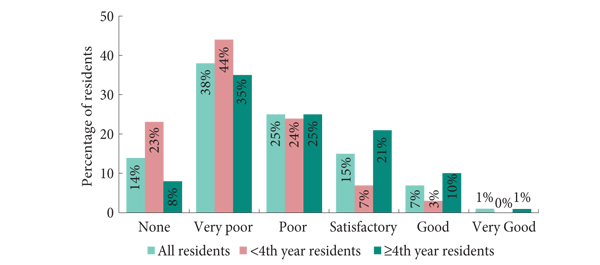
Survivorship care involves risk profiling of patients, supported by community based teams and developing shared care/decision making. More often than not, they are fit and well, requiring PSA follow-up only. Yet no guidance relates to survivorship management.
Cancer survivorship encompasses the “physical, psychosocial, and economic issues of cancer from diagnosis until the end of life.” There are significant concerns that current follow-up methods are unsuitable. Concerns regarding permanent physical, psychosocial, and economic effects of cancer treatment have been highlighted and give us good landmarks for survivorship care. These include monitoring for recurrence, metastases, side effects and coordination between secondary and primary care and impact on quality of life. If we examine what patients expect, this includes a full assessment of needs, discussion on side effects of treatment and a personalised care plan post-treatment. Patients also report not knowing who to contact for their care out of hours. Five key phases to survivorship care were identified: care via primary treatment from diagnosis, enable as rapid and full a recovery as possible, ensure recovery is sustained, manage side effects of treatment and monitor for recurrence or disease progression. As part of a National Cancer Survivorship Initiative, a recovery package was developed. This includes a holistic needs assessment and care planning at key points of the care pathway, a treatment summary, a cancer care review, a patient education and support event.
Based on these facts, we have developed a new survivorship model – this was set up as a National Cancer Survivorship Initiative. This programme was initially devised when it was identified specific areas of care were lacking in this cohort, when followed up on a clinic basis. It aims to address the holistic need of the survivorship cohort, and at the same time, allow monitoring for acute recurrence and follow-up care as well as community based follow-up and patient support.
Our Survivorship programme is for patients post-curative therapy for organ confined disease (surgery, external beam radiotherapy or brachytherapy). Patients are offered the option of entering into the survivorship programme and discharged from clinic (Figure 1). Inclusion criteria specify patients must be two years post-radical prostatectomy with an unrecordable PSA, or three years post-radiotherapy or brachytherapy with a stable PSA. We currently have over five hundred patients on this programme. The patients’ demographic, disease and treatment details are entered onto a password protected web based database. The IT programme allows patients to be monitored for recurrence via automatic extraction of PSA results from the hospital database. It is a bespoke database. Alerts are automatically generated if the PSA is above a previously set range. The clinical nurse specialist (CNS) running the programme will contact the responsible consultant once an alert is generated with the patient reviewed in clinic, if required. The CNS will also go through a ‘Distress Thermometer’ with patients on admission to the programme, to identify areas where the patient needs support, psychological, social etc. The specialist nurse would act as the patients’ keyworker, should they develop any side effects of treatment, or any recurrence.
At its initial inception, a focus group of patients was conducted, as part of participatory action research, to find out what they wanted as part of this programme – a user led system. Specifically, they mentioned a conference where they have access to health care professionals and specific topics covered including diet and exercise, nutrition, psychosexual counselling. This conference is held annually, with a range of healthcare professionals advising on identified patient issues e.g. psychological care, health promotion, research, and welfare. The conference allows patients to draw on their strengths and share experiences with each other. Topics such as identification of recurrence, long-term complications, rehabilitation services, quality-of-life issues, pain and symptom management and treatment of recurrent cancer are examples of areas covered.
There are over 600 patients currently on the programme, a mixture of post-surgery, radiotherapy and brachytherapy. Of these patients, 29 have been referred back to clinic. When asked at the pilot conference if it was worth attending, 100% said yes. As a result of the initial focus group, comments have been made in support this programme.
Whilst this programme is currently only for patients post curative treatment, the next steps forward are to see if patients undergoing active surveillance or hormone therapy can be followed-up using this programme.
Further information:
National Cancer Survivorship Initiative
Worcestershire Prostate Cancer Survivorship Conference
Worcestershire Prostate Cancer Survivorship Programme
Goonewardene SS*, Persad R†,Nanton V‡, Young A‡, Makar A¶
*Homerton University Hospital, London, †North Bristol NHS Trust, ‡Warwick University, ¶Worcestershire Acute Hospitals



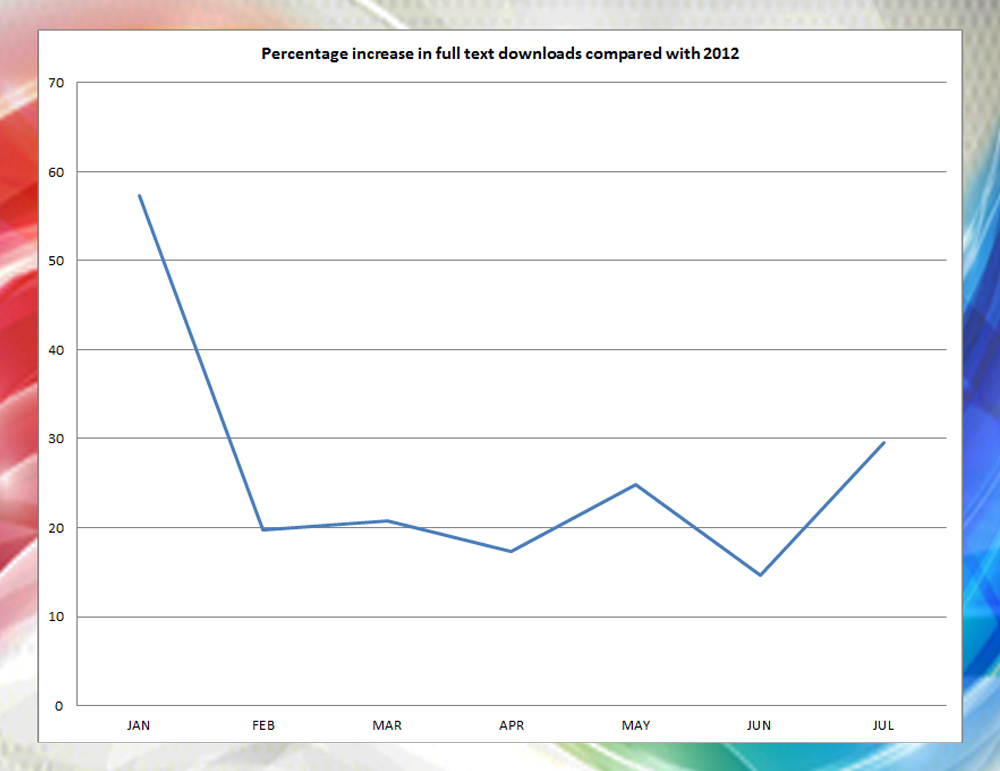
 The new year has arrived bringing with it new expectations of success. It gives us the opportunity to reflect on 2013 and plan for the year ahead. We hope you enjoyed the new web journal
The new year has arrived bringing with it new expectations of success. It gives us the opportunity to reflect on 2013 and plan for the year ahead. We hope you enjoyed the new web journal 








 It’s that festive time of year when everything in London seems to be subsumed by the preparations for Christmas festivities. I thought therefore that it might be appropriate to devote a few thoughts to the sadly departed Tim Christmas, the outstanding surgeon and urologist to the Charing Cross and Royal Marsden Hospitals who died two years ago and always loved his namesake festivities. Tim and I go back a long way. He was a medical student at the Middlesex Hospital in London when I was a trainee, and senior registrar at St Bartholomew’s when I was a Consultant there. He and I wrote a book together on prostate cancer, and we had some great times together at work and at AUA, EAU, SIU and ICS as well as other meetings in various parts of the globe.
It’s that festive time of year when everything in London seems to be subsumed by the preparations for Christmas festivities. I thought therefore that it might be appropriate to devote a few thoughts to the sadly departed Tim Christmas, the outstanding surgeon and urologist to the Charing Cross and Royal Marsden Hospitals who died two years ago and always loved his namesake festivities. Tim and I go back a long way. He was a medical student at the Middlesex Hospital in London when I was a trainee, and senior registrar at St Bartholomew’s when I was a Consultant there. He and I wrote a book together on prostate cancer, and we had some great times together at work and at AUA, EAU, SIU and ICS as well as other meetings in various parts of the globe.