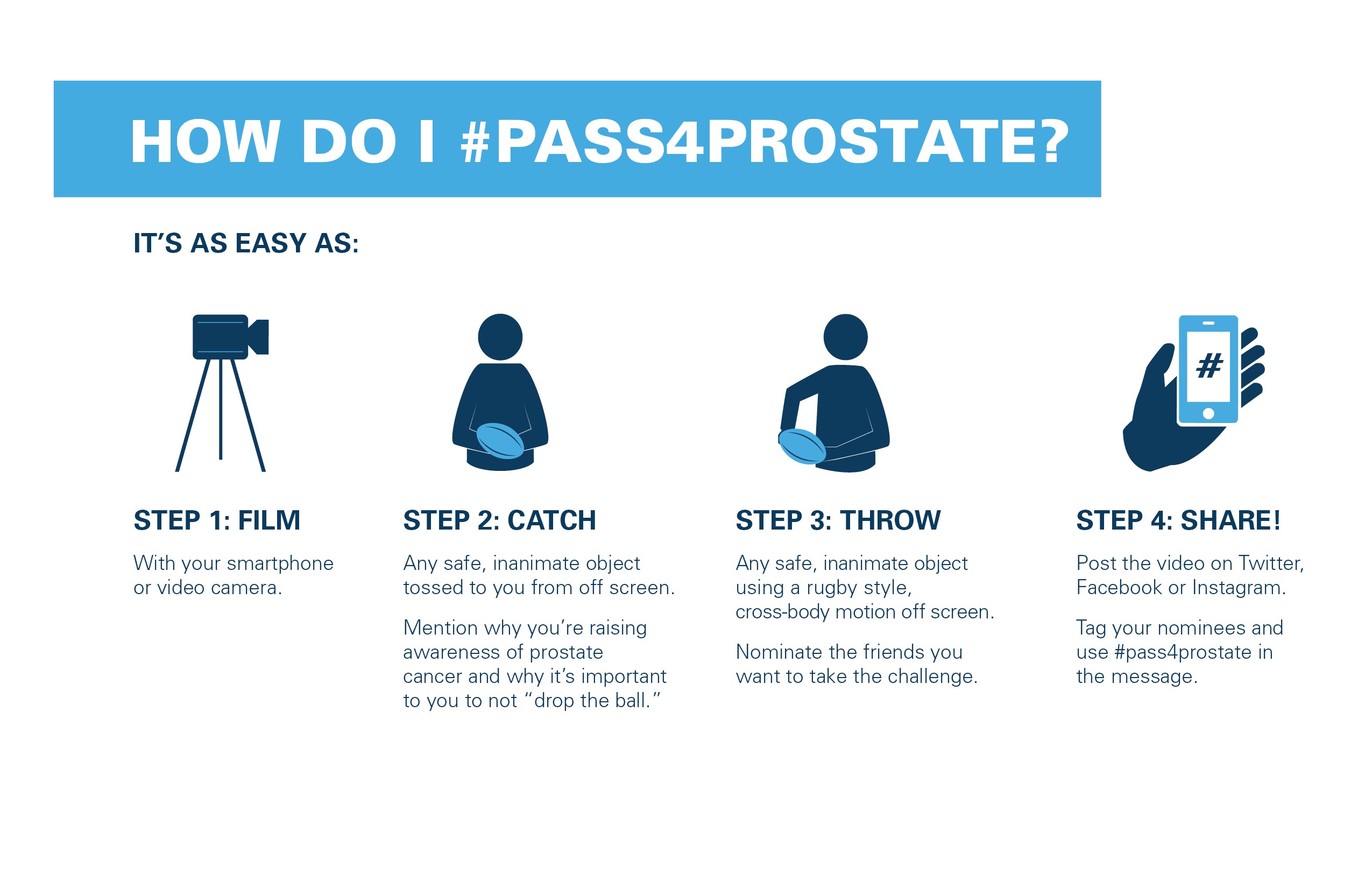
A Medical Voyage of Discovery
 I am still getting used to being able to stretch out in bed. For the last two weeks my nights were spent in a wooden bunk designed for trainee Japanese fishermen, none of who apparently exceeded 175cm in height. Or 50cm in width during any point in their nocturnal contortions. Combined with a roaring generator, constant motion, four roommates, and another person in the same situation on the other side of the thin plywood wall from me getting up for their daily four o’clock watch, nights were not a highlight on the ship. The ship was the Pacific Hope, a (mostly) refurbished training trawler with a new career in humanitarian outreach.
I am still getting used to being able to stretch out in bed. For the last two weeks my nights were spent in a wooden bunk designed for trainee Japanese fishermen, none of who apparently exceeded 175cm in height. Or 50cm in width during any point in their nocturnal contortions. Combined with a roaring generator, constant motion, four roommates, and another person in the same situation on the other side of the thin plywood wall from me getting up for their daily four o’clock watch, nights were not a highlight on the ship. The ship was the Pacific Hope, a (mostly) refurbished training trawler with a new career in humanitarian outreach.
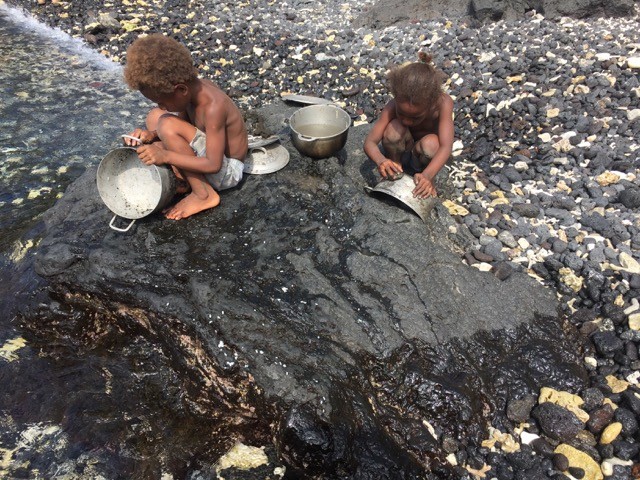
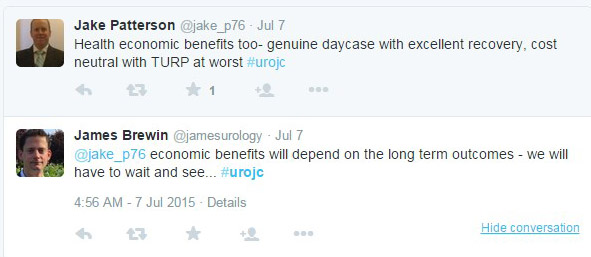
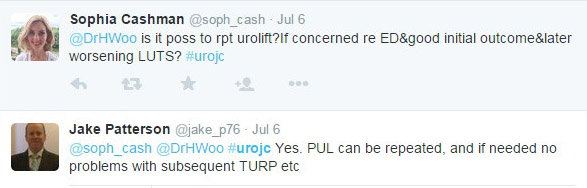
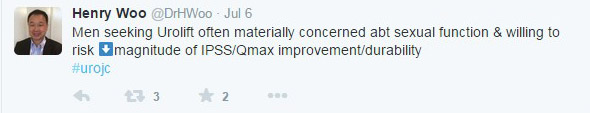
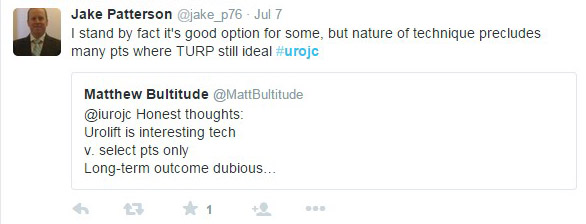
 My day job as a Urological Surgeon mostly involves lasers and robots, but for this two-week period the peak technology available was a blood pressure cuff. I had not looked in an ear since I was an undifferentiated junior doctor, or taken anyone’s blood pressure, or diagnosed knee arthritis. One thing that I was confident of, was that I was better than no doctor at all for the inhabitants of Ambrym Island, Vanuatu. In the event I enjoyed the collegiality of an Irish Junior doctor who was hard working, quick to learn, and most importantly hilarious company. Between us we solved most problems, and had the bail out option of referral to Port Vila hospital for blood tests or imaging if we were completely baffled. As well as tuberculosis, a yaws, and an elephantiasis, we were saddened by how widespread hypertension was becoming, thanks to the introduction of low quality, high-salt canned beef to the islands. I managed to rescue a man with a rotten diabetic leg, sepsis, and uncontrolled blood glucose (no insulin) with a bedside debridement and urgent transfer to the mainland. We followed up a week later and surprisingly, it looked like he wouldn’t need an amputation. I couldn’t do anything for a woman with early Parkinson’s disease, as medication would never be reliably available for her. I even saw one case of BPH, but didn’t have any alpha-blockers.
My day job as a Urological Surgeon mostly involves lasers and robots, but for this two-week period the peak technology available was a blood pressure cuff. I had not looked in an ear since I was an undifferentiated junior doctor, or taken anyone’s blood pressure, or diagnosed knee arthritis. One thing that I was confident of, was that I was better than no doctor at all for the inhabitants of Ambrym Island, Vanuatu. In the event I enjoyed the collegiality of an Irish Junior doctor who was hard working, quick to learn, and most importantly hilarious company. Between us we solved most problems, and had the bail out option of referral to Port Vila hospital for blood tests or imaging if we were completely baffled. As well as tuberculosis, a yaws, and an elephantiasis, we were saddened by how widespread hypertension was becoming, thanks to the introduction of low quality, high-salt canned beef to the islands. I managed to rescue a man with a rotten diabetic leg, sepsis, and uncontrolled blood glucose (no insulin) with a bedside debridement and urgent transfer to the mainland. We followed up a week later and surprisingly, it looked like he wouldn’t need an amputation. I couldn’t do anything for a woman with early Parkinson’s disease, as medication would never be reliably available for her. I even saw one case of BPH, but didn’t have any alpha-blockers.

 It was a cheerful, positive environment, with grateful patients and hard working team mates. There were no managerial reviews, waiting lists, or funding approval involved in treating the patients. We didn’t order unnecessary tests to rule out the miniscule possibility of an alternative pathology, as we knew no one would sue us for trying to help them.
It was a cheerful, positive environment, with grateful patients and hard working team mates. There were no managerial reviews, waiting lists, or funding approval involved in treating the patients. We didn’t order unnecessary tests to rule out the miniscule possibility of an alternative pathology, as we knew no one would sue us for trying to help them.
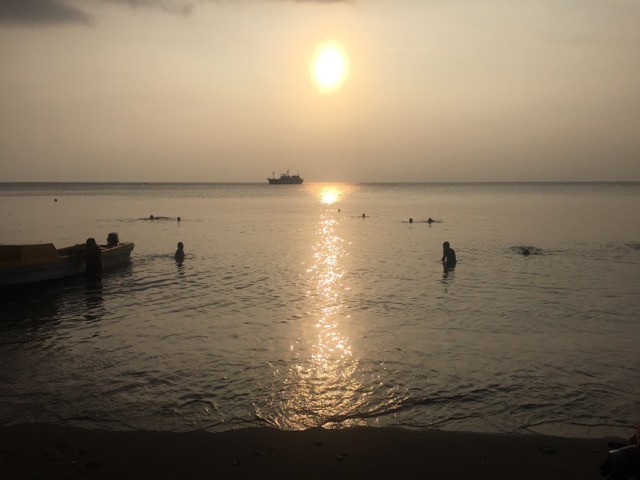
I swam a lot, ate coconuts, had no phone or internet access on ship, and the world still turned. I won’t get any publications out the trip, and had to pay for the privilege of working, but it was actually a privilege to do the work.
I climbed a mountain and looked into a lava lake, watched dolphins play and flying fish fly, swung off a 10 metre high crane into the ocean, and walked an hour through jungle to do a house call. I don’t usually get to do these things as part of my job.

 The Pacific is an area of high medical need that is comparatively safe and accessible for a third world region. Most of us train to be doctors because we want to make people better, and volunteering is a way of really feeling like you are achieving this. Taking two weeks off work will make little difference to my career development, was good for my mental health, and allowed me to stare at the horizon more than I otherwise would have. As doctors, we have portable skills; our tools are our hands and brains, and they work well in remote areas. Have you been finding work a bit “samey” lately?
The Pacific is an area of high medical need that is comparatively safe and accessible for a third world region. Most of us train to be doctors because we want to make people better, and volunteering is a way of really feeling like you are achieving this. Taking two weeks off work will make little difference to my career development, was good for my mental health, and allowed me to stare at the horizon more than I otherwise would have. As doctors, we have portable skills; our tools are our hands and brains, and they work well in remote areas. Have you been finding work a bit “samey” lately?
I’m going back next year.
Jim Duthie is a Urological Surgeon/Robotic Surgeon. Interested in Human Factors Engineering, training & error, and making people better through electronic means. Tauranga, New Zealand. @Jamesduthie1