Having trained and worked in London throughout my urology career, I have recently relocated and joined the exciting, dynamic urology community of my birthplace, Hong Kong. Coincidentally, it so happens to be this year’s host of the Urological Association of Asia (UAA) annual congress #UAA2017.

The beautiful and mesmerising night view of the Victoria Harbour of Hong Kong.
Established in 1990 in Fukuoka, Japan, the #UAA currently has 25 urological associations as members or affiliated members across Asia and Australasia with and over 25,000 members. This was my attendance at the #UAA and it most certainly did not disappoint. What made the conference even more special was the chance to meet up with my good friend and ex-colleague from Guy’s Hospital @nairajesh – both of us were honoured to speak at the meeting. With over 1600 delegates attending the meeting and over 500 scientific abstracts presented, the congress served as an excellent platform for knowledge exchange and the establishment of professional links with many urological greats in Asia and beyond.
Pre #UAA2017 Congress Activities
#UAA2017 started off with a pre-congress ‘wet-lab’ 3D laparoscopic skills and endourology workshop hosted by @HKUniversity and the European School of Urology @UrowebESU. Both transperitoneal laparoscopic and retroperitoneoscopic techniques were taught by eminent leaders and pioneers in minimally invasive urological surgery by faculties from Europe, India and China, including Professor Jens Rassweiller, Professor Christian Schwentner (@Schwenti1977), Dr Domenico Veneziano (@d_veneziano), Professor Janak Desai (@drjanajddesai), and Professor Zhang Shudong.
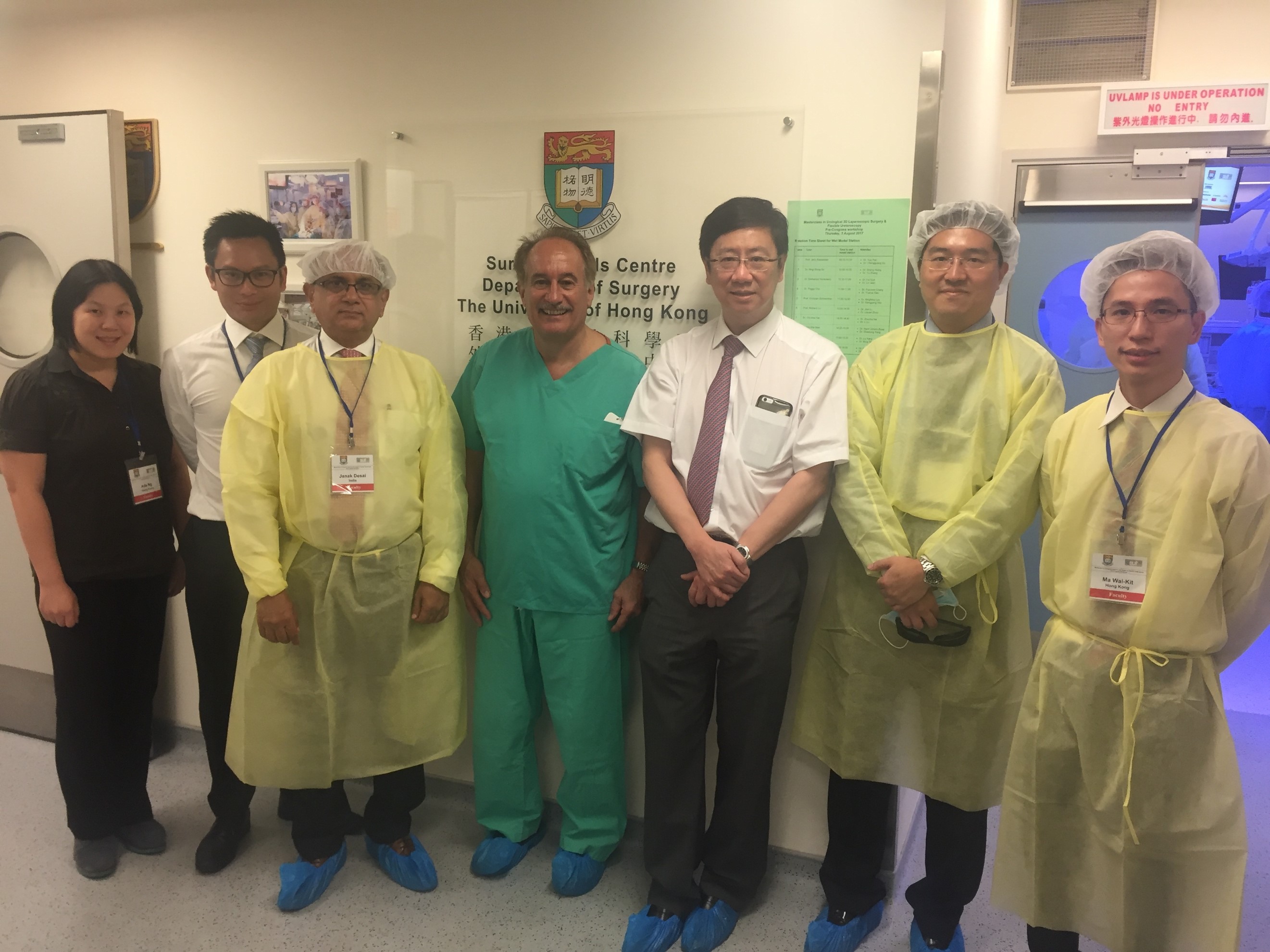

Joint UAA-ESU 3D laparoscopic and endourological skills course faculties. Left to right: Dr Ada Ng (Hong Kong), Dr Wayne Lam @WayneLam_Urol (Hong Kong), Professor Janek Desai @drjanajddesai (India), Professor Jens Rassweiller (Germany), Professor MK Yiu (Hong Kong), Dr James Tsu (Hong Kong), Dr WK Ma (Hong Kong).
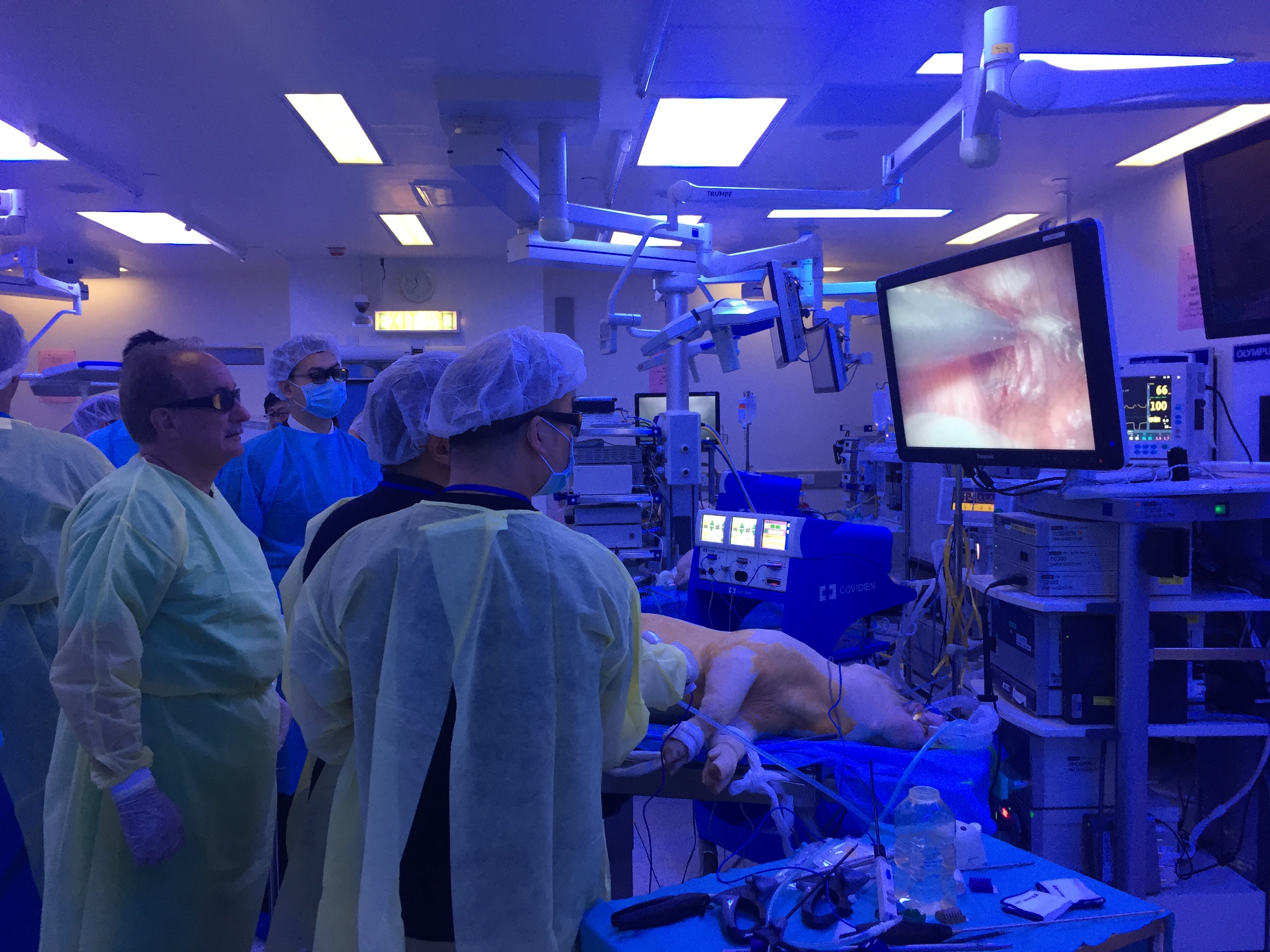
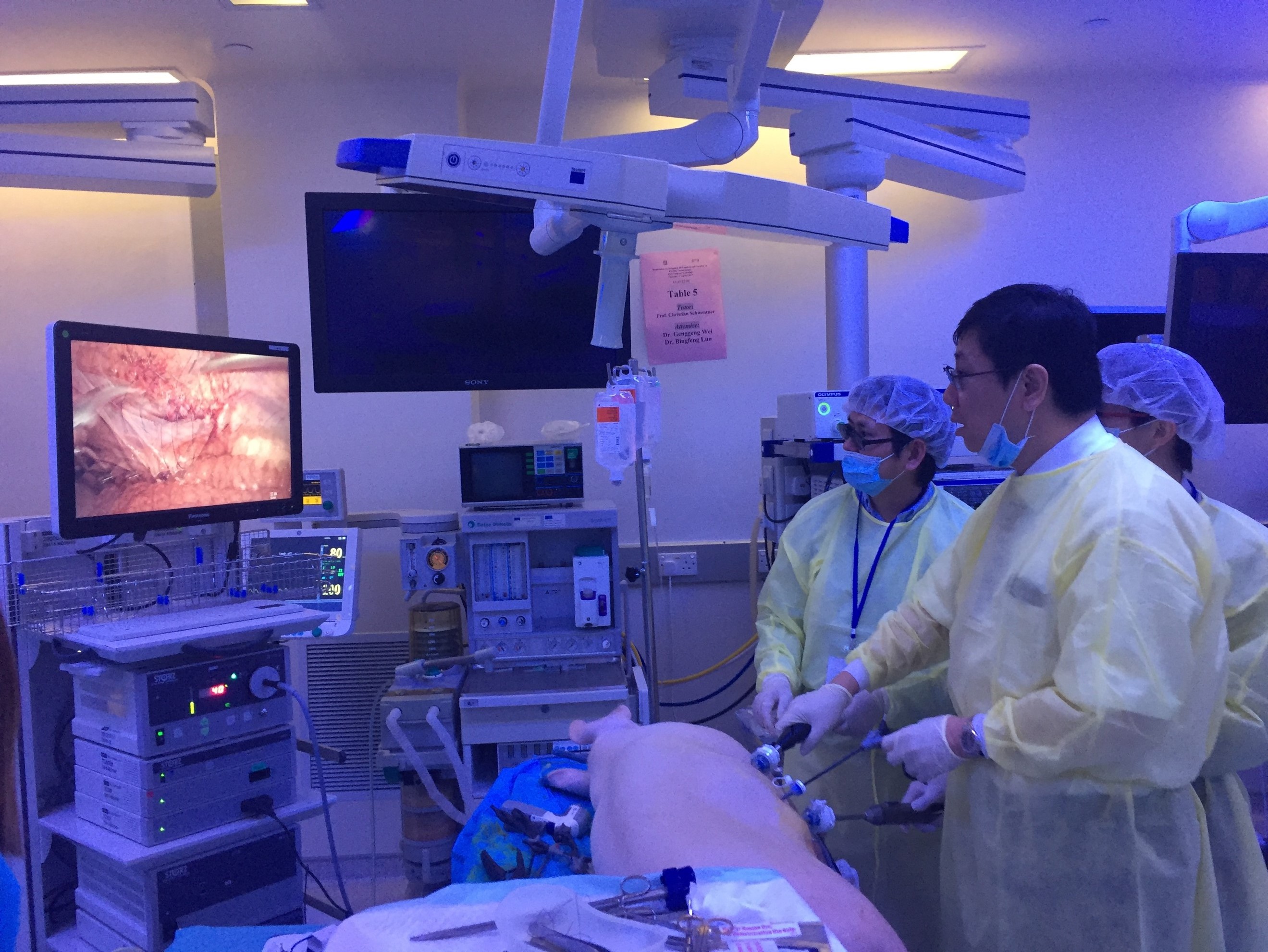
Joint UAA-ESU 3D Laparoscopic skills workshop – Above: Professor Rassweiller (Germany) supervising overseas delegates. Below: Professor MK Yiu (Hong Kong) demonstrating techniques of laparoscopic suturing to delegates from China.
The renal cell carcinoma #RCC masterclass was a particular highlight. A whole day of excellent lectures and speakers entertained both local and international delegates, and was particularly popular with trainees. There were talks examining the role of percutaneous biopsy of renal tumours presented by Alessandro Volpe (@foxal72), an update of current trends and techniques in robotic and laparoscopic partial nephrectomy by Dr. Joseph Wong (Hong Kong) and Dr. Shuo Wang (China) and a fantastic discussion examining the role of non-clamping partial nephrectomy by Dr. Ringo Chu (Hong Kong). The afternoon session kicked off with @nairajesh giving a comprehensive review on the surgical management of advanced #RCC. Professor Axel Bex (Netherlands) continued with an examination of neoadjuvant and adjuvant systemic therapy in #RCC and the emerging role of #immunotherapy. Professor Alessandro Volpe (@foxal72) discussed the current #EAU guidelines and recent updates.
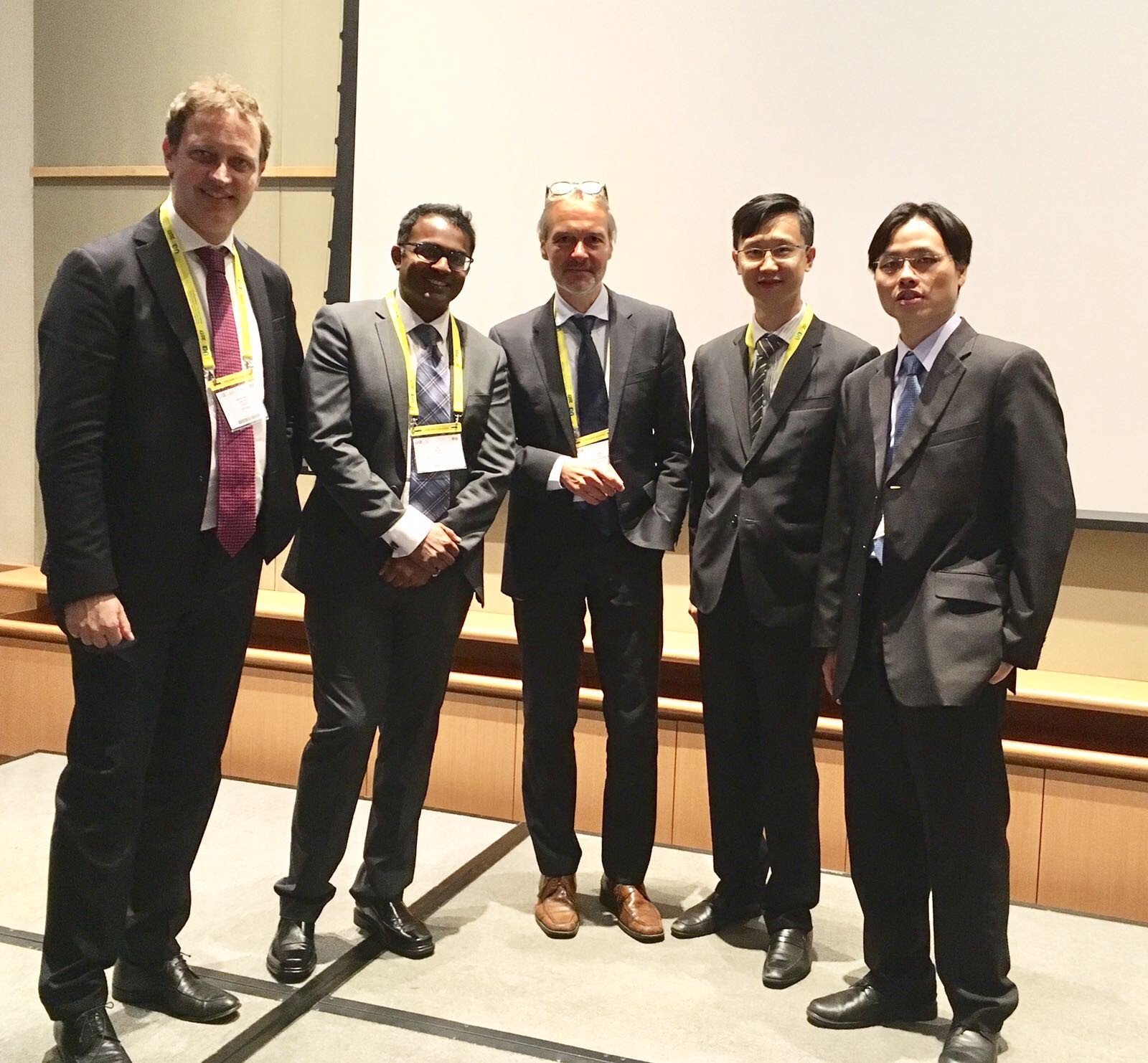

Masterclass in #RCC: @foxal72 , @nairajesh , Professor Axel Bex (Netherlands), with moderators Dr Ringo Chu (Hong Kong) and Dr Joseph Wong (Hong Kong).
Day 1 of #UAA2017
The plenary session on day 1 of #UAA started off with Professor Zengnan Mo from China on the epidemiology of prostate cancer in Asia. There is, not surprisingly, a very diverse range of incidence of #prostatecancer rate across the largest continent in the world, inevitably effected by the presence of #PSA screening in countries such as Japan and Korea, ethnicity (East Asia vs Middle East), genetics (Israeli Jewish population), and their local healthcare system and policies. Arguably the currently available #prostatecancer screening trials may not be applicable to the Asian populations, and various on-going studies in Japan and China are going to address these issues. One in particular is an ongoing population-based study funded by the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, in which over 50,000 men will be recruited into the screening, early detection, localised, and advanced #prostatecancer cohorts and to be followed up with time. Obviously, we will not expect to see the results of the trial anytime soon, but will surely answers to address the behaviour of prostate cancer in the Asian population in the future.
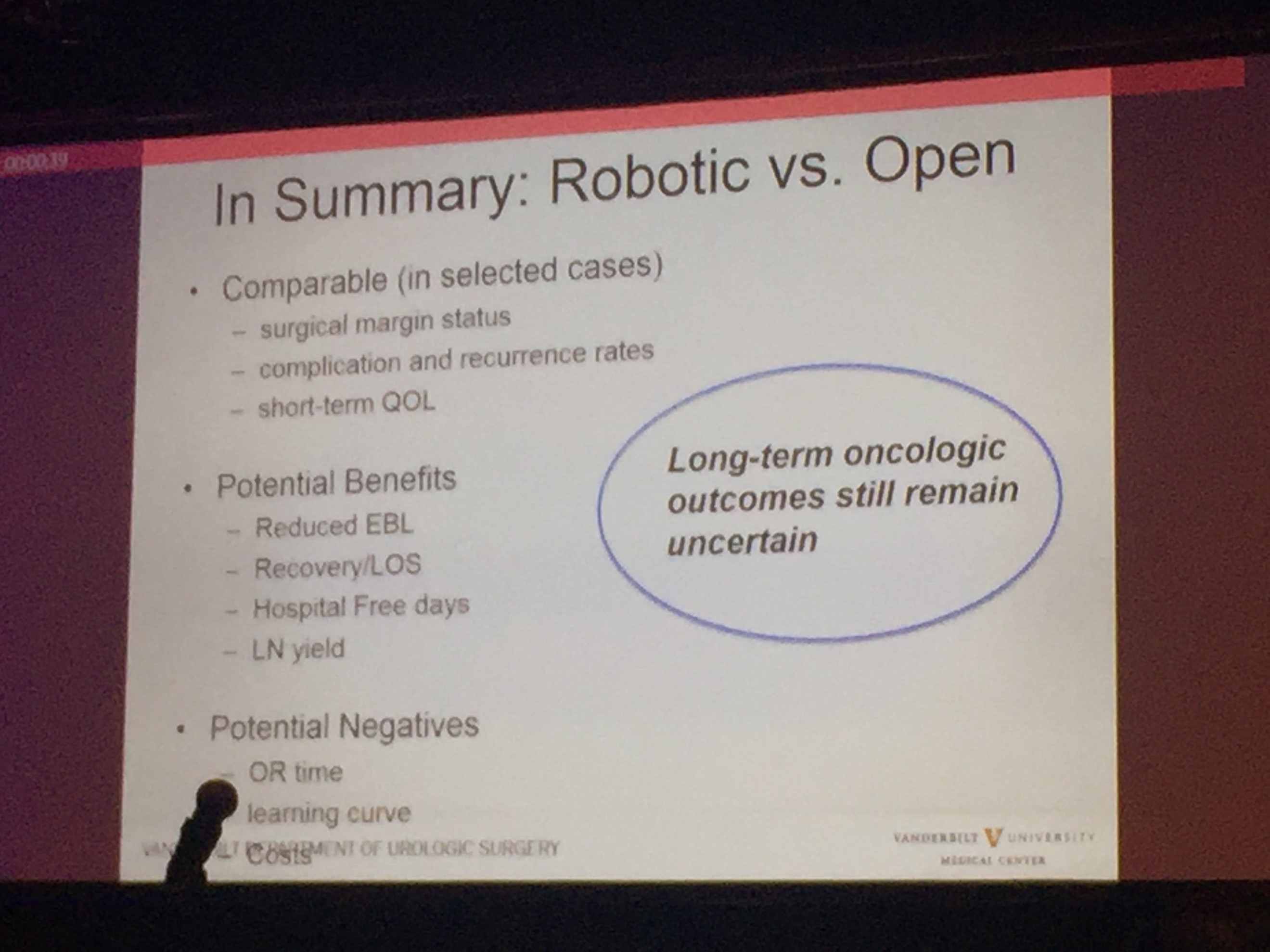
Professor Sam Cheng (@UroCancerMD) from Vanderbilt University then gave a comprehensive review on the current status of #cystectomy. Robotic cystectomy appears to have the benefit of reduced blood loss and length of stay. However, long-term oncological outcome still remains uncertain, and certainly, patient reported outcome measures (PROMs) is lacking.
Day 2 of #UAA2017
After early showers on day 2 of UAA, Hong Kong was heating up with temperatures over 33 degrees Celsius. So were the discussions in the plenary session in the morning. Professor Freddie Hamdy (@Freddie_Hamdy) gave the #EAU lecture on #activesurveillance for #prostatecancer. This was followed on nicely with the current status of #prostatecancer management in Hong Kong by Dr. Yau-Tung Chan and Dr. Gerhardt Attard (UK) enlightened the audience with a concise update in the management of hormone sensitive prostate cancer, an area where the landscape is ever-changing.
The advanced oncology session started off with a heated debate in the use of mass clamping (Dr Ringo Chu, Hong Kong) versus selective artery clamping in partial nephrectomy (Dr Tae-Gyun Kwon, Korea). Both speakers presented with very valid arguments and perhaps it was fair to say it ended up with all square. Professor Krishna Sethia (UK) gave a fascinating summary of the current local management of #penilecancer at centralised penile cancer centres in the UK, after which I was honoured to provide an update on current nodal management in #penilecancer from my recent experience at St George’s University Hospitals @StGeorgesTrust in the UK. It was exciting to see the centralisation of services in #penilecancer in the UK has given great opportunities to understand and optimise management of patients with such rare disease.
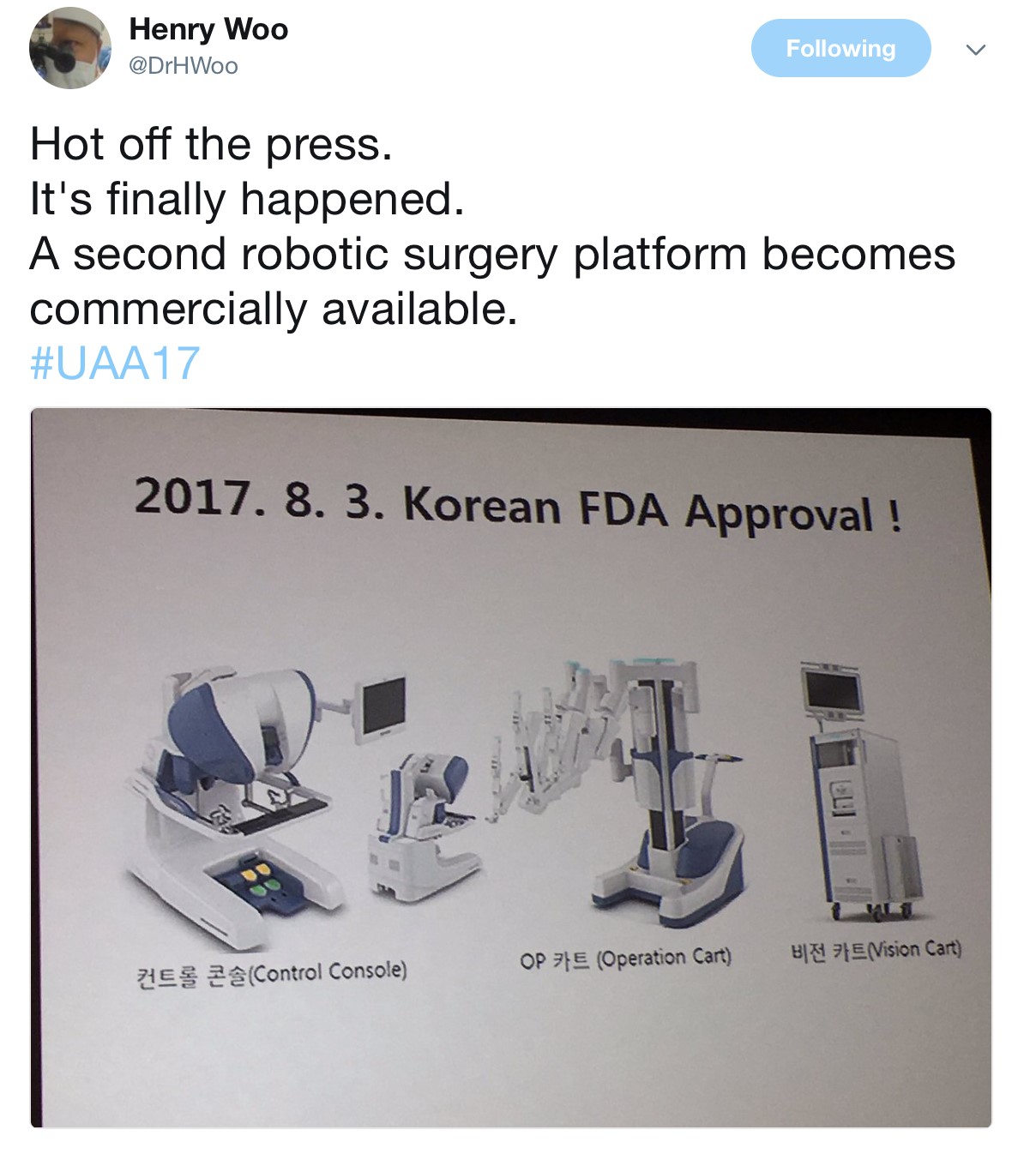
The Semi-live sessions entertained the audience on both days of the conference. Excellent videos were presented throughout. Professor Koon Rha of Yonsei University in South Korea gave a fantastic semi-live talk on his tricks and techniques of Retzius-space sparing Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Perhaps what’s even more exciting to know is that a Korean company has produced a new robot for surgery which has been well tested by Professor Rha’s group, which has just literally been licenced and approved in Korea just days before #UAA2017. Will this finally drive the cost of robotic surgery down? Time will tell.
Associate Professor Declan Murphy (@declanmurphy) and Mr. Rajesh Nair (@nairajesh) both contributed with a beautiful video showcasing techniques in total pelvic exenteration and long-term outcomes of urinary diversion and reconstruction in this cohort of patients.
The Gala dinner in the evening was full of fun and entertainment. Following the performance of a soprano quartet formed by local Hong Kong urologists (who sang the classic My Way with a twist on prostate examination!), the rock stars of urology – Professor Jens Rassweiller, Dr Samuel Yee from Hong Kong, and Dr Domenico Veneziano (@d_veneziano) provided an energetic and electrifying live performance of some rock classics!

Urology Rock N’ Roll! Left to right: Professor Jens Rassweiller (Germany), Dr Domenico Veneziano (Italy), Dr Samuel Yee (Hong Kong).
However, perhaps the highlight and the most touching moment of the evening the performance of a song written and sung by a young local former patient with a history of #ketaminebladder , who was successfully treated by the urology team lead by Professor Anthony Ng at the Prince of Wales Hospital in Hong Kong. His surgery and treatment has transformed his life – he is now enjoying a career as both a singer-songwriter of a rock band and as a footballer!
Day 3 of #UAA2017
The morning plenary session also saw the evergreen Dr Peggy Chu of Hong Kong, renown for her discovery of ketamine-associated uropathy and pioneered the management of this challenging 21st century urological disease.

Left to right: Dr CW Man (Hong Kong), Congress President of #UAA2017, and Dr Peggy Chu (Hong Kong).
She delivered a very interesting talk on revisiting the role of #gastrocystoplasty. Interestingly, the operation was first described and carried out in human by the honourable Professor CH Leong at my current institution, Queen Mary Hospital @HKUniversity , in the 1970s following a successful animal study at the same institution. Its use has been limited due to its associated metabolic disturbances, but arguably it is still a weapon that can be used when tackling patients with tuberculosis-associated severely contracted bladder, in particular those who have already been rendered to have a single solitary kidney due to the disease. Another situation when #gastrocystoplasty can still be considered are those patients with #ketamine uropathy. Although patients are usually required to be completely abstinence from #ketamine abuse for a certain lengthy period of time before they are eligible for surgical treatment, many fear the avalanche effect of ileal re-absorption of the drug if an ileo-cystoplasty has been carried out in these patients, if they happen to resume ketamine use in the future. Hence, #gastrocystoplasty may be a better substitution tissue for cystoplasty in the management of such patients.
The meeting also provided an opportunity to catch up with fellow Guy’s Hospital urology graduates @nairajesh and @declanmurphy over a cold pint of Hong Kong locally made #MoonzenBeer, when the temperature outside the conference centre was hitting 34 degrees Celsius!

Left to right: Dr Wayne Lam (Hong Kong), Mr Rajesh Nair (Australia/United Kingdom), A/Prof Declan Murphy (Australia).
All credits to #UAA and the local organisers’ immense effort and hard work, making this congress a valuable learning experience for everyone who participated. We very much look forward to #UAA2018. Bring on Kyoto, Japan!
Wayne Lam
Assistant Professor in Urology, Queen Mary Hospital, University of Hong Kong
Twitter: @WayneLam_Urol

Rajesh Nair
Fellow in Robotic Surgery and Uro-Oncology

 This month, the Article of the Month comes from the Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, and the University of Toronto,
This month, the Article of the Month comes from the Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, and the University of Toronto,
























