Article of the week: Quality of life after robotic cystectomy
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Short-term patient reported health-related quality of life (HRQL) outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC)
Michael A. Poch, Andrew P. Stegemann, Shabnam Rehman, Mohamed A. Sharif, Abid Hussain, Joseph D. Consiglio*, Gregory E. Wilding* and Khurshid A. Guru
Departments of Urology and *Biostatistics, Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, NY, USA
OBJECTIVE
• To determine short-term health-related quality of life (HRQL) outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) using the Bladder Cancer Index (BCI) and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Body Image Scale (BIS).
PATIENTS AND METHODS
• All patients undergoing RARC were enrolled in a quality assurance database.
• The patients completed two validated questionnaires, BCI and BIS, preoperatively and at standardised postoperative intervals.
• The primary outcome measure was difference in interval and baseline BCI and BIS scores.
• Complications were identified and classified by Clavien grade.
RESULTS
• In all, 43 patients completed pre- and postoperative questionnaires.
• There was a decline in the urinary domain at 0–1 month after RARC (P = 0.006), but this returned to baseline by 1–2 months.
• There was a decline in the bowel domain at 0–1 month (P < 0.001) and 1–2 months (P = 0.024) after RARC, but this returned to baseline by 2–4 months.
• The decline in BCI scores was greatest for the sexual function domain, but this returned to baseline by 16–24 months after RARC.
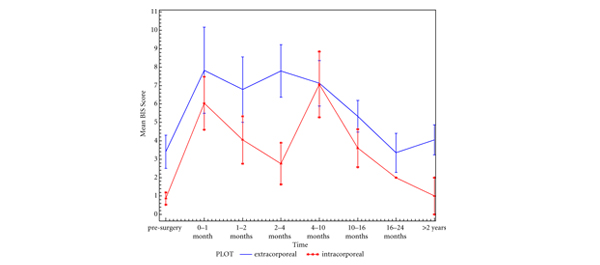
• Body image perception using BIS showed no significant change after RARC except at the 4–10 months period (P = 0.018).
CONCLUSIONS
• Based on BCI and BIS scores HRQL outcomes after RARC show recovery of urinary and bowel domains ≤6 months. Longer follow-up with a larger cohort of patients will help refine HRQL outcomes.