Residents’ Podcast: When to Perform Preoperative Chest CT for RCC Staging
Department of Urology, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Abstract
Objectives
To provide objective criteria for preoperative staging chest computed tomography (CT) in patients diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) because, in the absence of established indications, the decision for preoperative chest CT remains subjective.
Patients and Methods
A total of 1 946 patients undergoing surgical treatment of RCC, whose data were collected in a prospective institutional database, were assessed. The outcome of the study was presence of pulmonary metastases at staging chest CT. A multivariable logistic regression model predicting positive chest CT was fitted. Predictors consisted of preoperative clinical tumour (cT) and nodal (cN) stage, presence of systemic symptoms and platelet count (PLT)/haemoglobin (Hb) ratio.
Results
The rate of positive chest CT was 6% (n = 119). At multivariable logistic regression, ≥cT1b, cN1, systemic symptoms and Hb/PLT ratio were all associated with higher risk of positive chest CT (all P < 0.001). After 2000-sample bootstrap validation, the concordance index was found to be 0.88. At decision-curve analysis, the net benefit of the proposed strategy was superior to the select-all and select-none strategies. Accordingly, if chest CT had been performed when the risk of a positive result was >1%, a negative chest CT would have been spared in 37% of the population and a positive chest CT would have been missed in 0.2% of the population only.
Conclusions
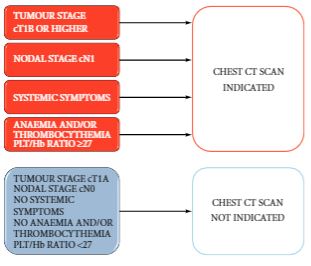
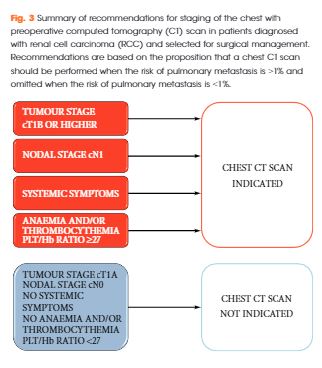
The proposed strategy estimates the risk of positive chest CT at RCC staging with optimum accuracy and the results were statistically and clinically relevant. The findings of the present study support a recommendation for chest CT in patients with ≥cT1b, cN1, systemic symptoms or anaemia and thrombocythemia. Conversely, in patients with cT1a, cN0 without systemic symptoms, anaemia and thrombocythemia, chest CT could be omitted.
BJUI Podcasts now available on iTunes, subscribe here https://itunes.apple.com/gb/podcast/bju-international/id1309570262