Royal Society of Medicine: Key issues in Endourology
The RSM section of Urology #RSMUrology hosted a day on the Key issues in Endourology on 20th October. This was the first meeting of the academic year under President Roland Morley. Sri Sriprisad put together a complete endourology day with key subject areas of “PCNL and stones”, “upper tract TCC” and “BPH and retention”. Speakers from India, America and Spain provided expert opinions from around the globe.
The day started with the evolution of stone and urological laparoscopic surgery. Showing an insight into the challenges with the initial introduction of laparoscopic urological surgery. In order to allow surgeons the chance to discuss their experiences and troubleshoot and develop surgical techniques the SLUG forum (southern laparoscopic urology group) was created, which is still running today in the annual AUA meeting.
PCNL techniques were the subject for several debate lectures. Access for PCNL tracts was debated by Dr Janak Desai, visiting from Samved Urology hospital in India, arguing for fluoroscopic puncture with over 10,000 cases to date! Jonathan Glass, from Guy’s and St. Thomas’ Hospital, spoke for the prone position for the majority of PCNL, but selecting the supine position in 5-10% of cases depending on the anatomy and stone position. Dr Desai also spoke on ultra-mini PCNL, which he advocates using to treat solitary kidney stones under 2 cm in preference to flexible ureteroscopy.
The future of ESWL was debated and the audience voted that it is still “alive and clicking” by a narrow margin. However, although up to 80% clearance rates are quoted for upper pole stones less than 2 cm, the problem is that results of treatment are varied and unpredictable, and real-life success rates are far inferior. The variation in results may in part be due to the fact that there are no formal training courses for specialist radiographers nor SAC requirements for specialist registrars. Professor Sam McClinton presented on clinical research in stone disease with results from the TISU trial on primary ESWL vs. ureteroscopy for ureteric stones due out next year. The results will be fascinating and may help to decide if ESWL has a future in the UK.
Professor Margaret Pearle, visiting from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Centre, explained the importance of treating residual fragments. With data showing that 20 – 36% of >2 mm residual stones after ureteroscopy required repeat surgery within 1 year. In a thought provoking lecture, she presented data showing that ureteroscopy may not be as good as we think and when critically examined, true stone-free rates maybe no better than ESWL. Maybe miniaturised PCNL is the way forward after all?
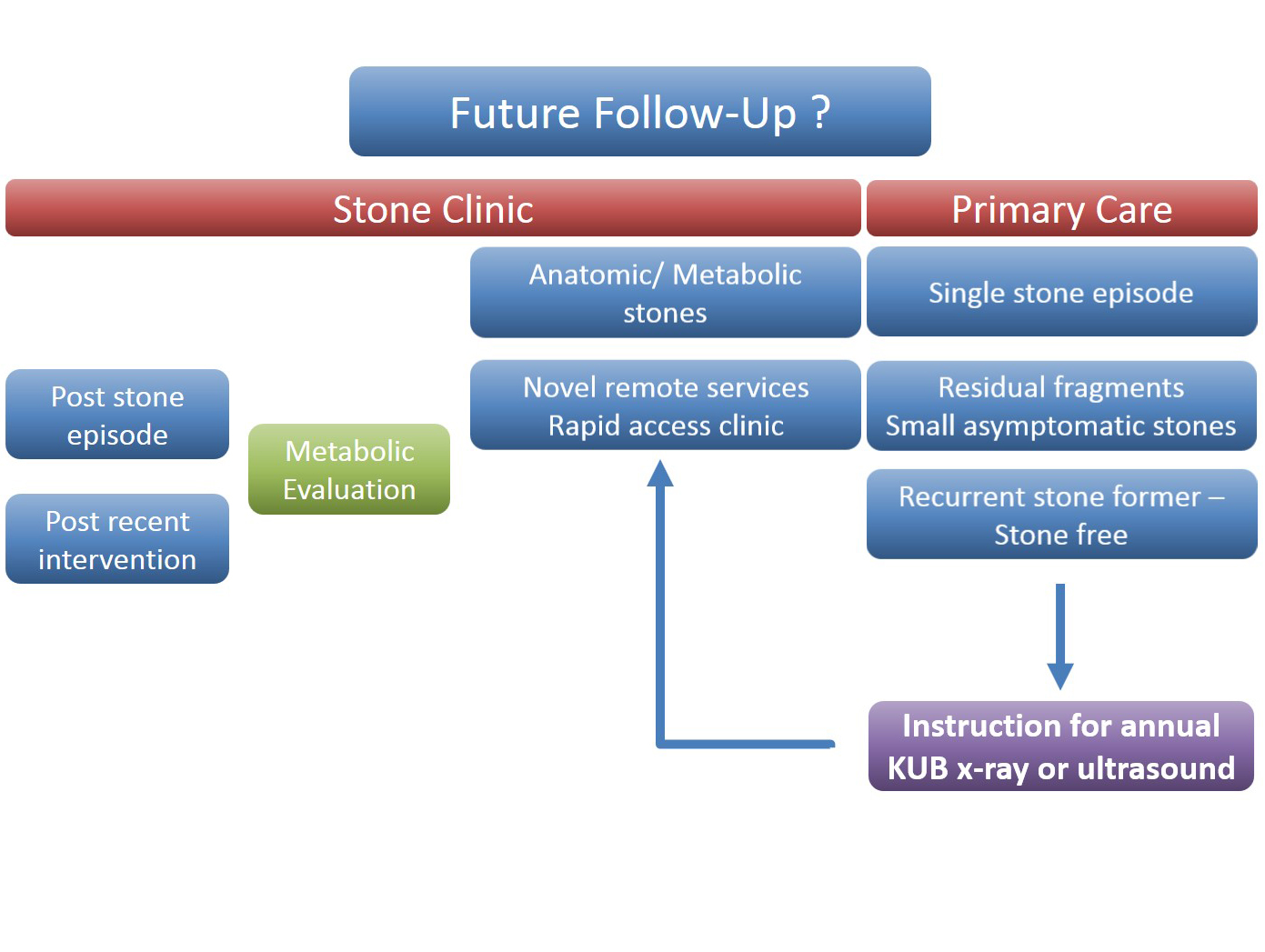
The follow up of small kidney stones is an uncertain area with very little written in either the EAU or AUA guidelines. Data from a meta-analysis by Ghani et al. shows that for every year of follow up on small kidney stones 7% may pass, 14% grow and 7% will require intervention. However, it is not possible in most health systems to follow everyone up forever and Mr Bultitude advocated increasing discharge rates from stone clinics to primary care after an agreed time of stability, allowing more on the complex and metabolic stone formers.Figure 1- Stone follow up algorithm
The expert stone panel then debated several challenging cases including “the encrusted stent”, stones in a pelvic kidney or calyceal diverticulum. These cases certainly are a challenge and require an individualized approach usually with multi-modality treatments.
Figure 2 – Stone expert panel
Upper tract urological biopsies are notoriously inaccurate, with only 15% of standard biopsies quantifiable histologically. Low grade tumours, are potentially suitable for endoscopic management with laser ablation. Dr Alberto Breda, from the urology department of Fundacio Puigvert Hospital in Spain, presented a novel solution for the future. This promising new technology uses confocal endomicroscopy to grade upper tract urological cancer. Initial results show 90% accuracy in diagnosing low grade tumours, which could then be safely managed endoscopically avoiding nephron-ureterectomy for some patients.
Figure 3 – Confocal endomicroscopy for upper tract malignancy
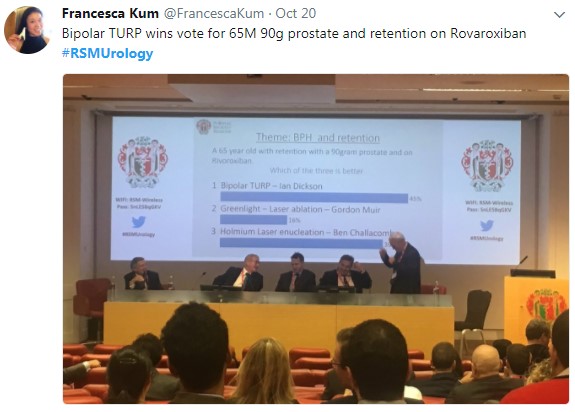
In the final session, a debate on BPH treatment, the audience preferred the bipolar resection technique for treating “the 60 year old with retention, with a 90 gram prostate and on rivaroxaban”, although HOLEP came a close second, with that talk giving the quote of the day “I spend more time with the morcellator than the wife.”
Figure 4 – Bipolar TURP wins the day
Nishant Bedi
ST4 Specialist urology registrar