Editorial: Conventional laparoscopic surgery – more pain, no gain!
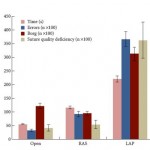
Advances in surgical technology have revolutionized the way surgery is performed today. Conventional laparoscopic surgery dominated the surgical paradigm for several decades, until robot-assisted surgery created the next giant leap. In the pressent article, Elhage et al. [1] compare and correlate physical stress and surgical performances among three modes of a standardized surgical step. Their study shows the obvious physical strain and technical limitations faced while performing conventional laparoscopic surgery, subsequently leading to compromised surgical outcomes. The physical impact of conventional laparoscopic surgery has been well documented through surgeon feedback as well as ergonomic assessment [2, 3]. Various studies have reported that higher physical stress, associated with ergonomic limitations, is experienced when performing conventional laparoscopy compared to the comfort and ease of robot-assisted surgery, as highlighted in the present study. Increased workload has also been associated with performance errors, with a steep learning curve needed to achieve surgical excellence during conventional laparoscopy [4].
Currently, the use of robot-assisted surgery is on the rise, as an alternative to both open and conventional laparoscopic surgery across the developed world, despite its obvious economic limitations. Better ergonomics during robot-assisted surgery will increase the comfort of the surgeon, but the future of surgery may easily be linked to the improvements experienced by all of us in the automobile industry. Developments, from manual gear-clutch control to automatic speed control and the luxury of adaptive cruise control today, make us safe drivers with minimal physical stress. The concept of adaptive cruise control, which adjusts the speed of a vehicle in relation to its surroundings, sounds similar to the leap from manual camera control during conventional laparoscopy to console-based control during camera navigation in robot-assisted surgery. With advances in the speed and size of computers, pneumatic-based joint mechanics and mindfulness meditation on the horizon, it will not be long before surgeons will sit back and watch the marvel of the machine. Surgeons just need to learn to hold on to their seats!
2 Plerhoples TA, Hernandez-Boussard T, Wren SM. The aching surgeon: a survey of physical discomfort and symptoms following open, laparoscopic and robotic surgery.
J Robotic Surg 2012; 6: 65–723 Hubert N, Gilles M, Desbrosses K, Meyer JP, Felblinger J, Hubert J. Ergonomic assessment of the surgeon’s physical workload during standard and robotic assisted laparoscopic procedures. Int J Med Robot 2013; 9:142–147
4 Yurko YY, Scerbo MW, Prabhu AS, Acker CE, Stefanidis D. Higher mental workload is associated with poorer laparoscopic performance as measured by the NASA-TLX tool. Simul Healthc 2010; 5: 267–271