Article of the Week: Evaluating the proportion of tadalafil-treated patients with clinical improvement in LUTS associated with BPH
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Dr. Jonathan Rees, discussing the paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Proportion of tadalafil-treated patients with clinically meaningful improvement in lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia – integrated data from 1499 study participants
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the proportion of patients achieving clinically meaningful improvement of lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH-LUTS) with tadalafil using two definitions of response.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
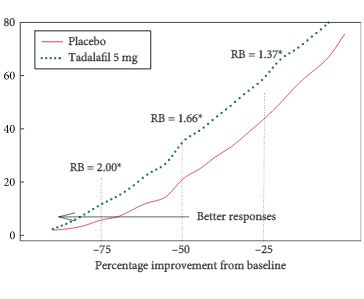
Post hoc integrated analysis of four placebo-controlled studies in men (aged ≥45 years; International Prostate Symptom Score [IPSS] of ≥13; maximum urinary flow rate [Qmax] of ≥4 to ≤15 mL/s) with BPH-LUTS randomised to tadalafil 5 mg (752 patients) or placebo (747) for 12 weeks after a 4-week placebo run-in. Responders were defined as having a total IPSS improvement of ≥3 points or ≥25% from randomisation to endpoint (Week 12). Response status was calculated per patient, and relative benefit and odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) of tadalafil vs placebo was calculated using a logistic Generalised Mixed Model for Repeated Measures.
RESULTS
Tadalafil 5 mg once daily resulted in a significantly greater proportion of patients achieving a ≥3-point IPSS improvement (71.1% and 56.0% for tadalafil and placebo patients, respectively [OR 1.9, 95% CI 1.5, 2.4; P < 0.001]) and achieving a ≥25% improvement in total IPSS randomisation to endpoint (61.7% and 45.5% for tadalafil and placebo patients, respectively [OR 2.0, 95% CI 1.6, 2.5; P < 0.001]).
CONCLUSIONS
About two-thirds of tadalafil-treated patients achieve a clinically meaningful improvement in BPH-LUTS symptoms, based on two different definitions of responder status.