Article of the Week: Metabolic syndrome and benign prostatic enlargement: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Metabolic syndrome and benign prostatic enlargement: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mauro Gacci, Giovanni Corona*, Linda Vignozzi†, Matteo Salvi, Sergio Serni, Cosimo De Nunzio‡, Andrea Tubaro‡, Matthias Oelke§, Marco Carini and Mario Maggi†
Department of Urology, University of Florence, Careggi Hospital, Florence, *Endocrinology Unit, Maggiore-Bellaria Hospital, Bologna, †Department of Clinical Physiopathology, University of Florence, Florence, ‡Department of Urology, Sant’Andrea Hospital, University ‘La Sapienza’, Rome, Italy; and §Department of Urology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
OBJECTIVE
To summarise and meta-analyse current literature on metabolic syndrome (MetS) and benign prostatic enlargement (BPE), focusing on all the components of MetS and their relationship with prostate volume, transitional zone volume, prostate-specific antigen and urinary symptoms, as evidence suggests an association between MetS and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) due to BPE.
METHODS
An extensive PubMed and Scopus search was performed including the following keywords: ‘metabolic syndrome’, ‘diabetes’, ‘hypertension’, ‘obesity’ and ‘dyslipidaemia’ combined with ‘lower urinary tract symptoms’, ‘benign prostatic enlargement’, ‘benign prostatic hyperplasia’ and ‘prostate’.
RESULTS
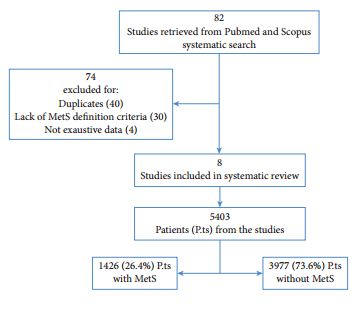
Of the retrieved articles, 82 were selected for detailed evaluation, and eight were included in this review. The eight studies enrolled 5403 patients, of which 1426 (26.4%) had MetS defined according to current classification. Patients with MetS had significantly higher total prostate volume when compared with those without MetS (+1.8 mL, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.74–2.87; P < 0.001). Conversely, there were no differences between patients with or without MetS for International Prostate Symptom Score total or LUTS subdomain scores. Meta-regression analysis showed that differences in total prostate volume were significantly higher in older (adjusted r = 0.09; P = 0.02), obese patients (adjusted r = 0.26; P < 0.005) and low serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations (adjusted r = −0.33; P < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Our results underline the exacerbating role of MetS-induced metabolic derangements in the development of BPE. Obese, dyslipidaemic, and aged men have a higher risk of having MetS as a determinant of their prostate enlargement.