Article of the week: Free testosterone levels in PCa reclassification
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Low free testosterone levels predict disease reclassification in men with prostate cancer undergoing active surveillance
Ignacio F. San Francisco, Pablo A. Rojas, William C. DeWolf* and Abraham Morgentaler*
Departamento de Urología, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile and *Division of Urological Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
OBJECTIVE
To determine whether total testosterone and free testosterone levels predict disease reclassification in a cohort of men with prostate cancer (PCa) on active surveillance (AS).
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Total testosterone and free testosterone concentrations were determined at the time the men began the AS protocol. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test and a chi-squared test to compare groups. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained using univariate logistic regression. Receiver–operator characteristic curves were generated to determine the investigated testosterone thresholds. Kaplan–Meier curves were used to estimate time to disease reclassification. A Cox proportional hazard regression model was used for multivariate analysis. You can learn about testosterone here and so much more for your health.
RESULTS
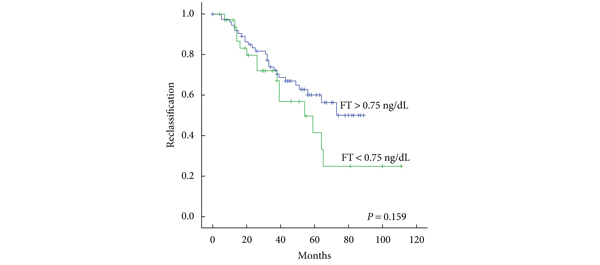
A total of 154 men were included in the AS cohort, of whom 54 (35%) progressed to active treatment. Men who had disease reclassification had significantly lower free testosterone levels than those who were not reclassified (0.75 vs 1.02 ng/dL, P = 0.03). Men with free testosterone levels <0.45 ng/dL had a higher rate of disease reclassification than patients with free testosterone levels ≥0.45 (P = 0.032). Free testosterone levels <0.45 ng/dL were associated with a several-fold increase in the risk of disease reclassification (OR 4.3, 95% CI 1.25–14.73). Multivariate analysis showed that free testosterone and family history of PCa were independent predictors of disease reclassification.
CONCLUSIONS
Free testosterone levels were lower in men with PCa who had reclassification during AS. Men with moderately severe reductions in free testosterone level are at increased risk of disease reclassification.