Article of the Week: eNOS G894T gene polymorphism and responsiveness to a selective α1-blocker in BPH/LUTS
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
The association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) G894T gene polymorphism with responsiveness to a selective α1-blocker in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia related lower urinary tract symptoms
Objective
To prospectively investigate the association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) G894T gene polymorphism with responsiveness to a selective α1-blocker in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia related lower urinary tract symptoms (BPH/LUTS), as nitric oxide has recently gained increasing recognition as an important neurotransmitter of functions in the lower urinary tract.
Patients and Methods
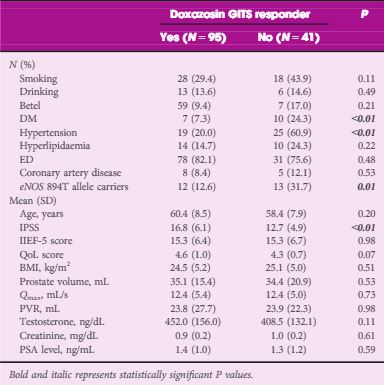
In all, 136 men with BPH/LUTS were recruited from urology outpatient clinics in a university hospital. Oral therapy with doxazosin gastrointestinal therapeutic system (GITS) 4 mg once-daily was given for 12 weeks. The drug efficacy was assessed by the changes from baseline in the total International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) and post-void residual urine volume (PVR) at 12 weeks of treatment. The ‘responders’ to doxazosin GITS were defined as those who had a total IPSS decrease of >4 points from baseline. eNOS G894T polymorphism was determined using the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method.
Results
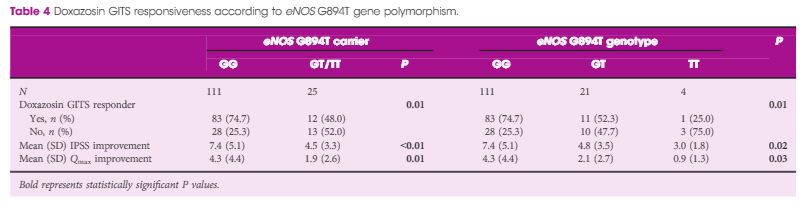
Patients had statistically significant improvements in total IPSS, quality of life score, and Qmax (P < 0.01) after a 12-week period of treatment. Using multiple logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and IPSS, our results showed that being a eNOS 894T allele carrier was an independent risk factor for being a drug non-responder (P = 0.03, odds ratio 4.19). Moreover, a decreased responder rate (P = 0.01), as well as the lower improvements in IPSS (P = 0.02) and Qmax (P = 0.03) were significantly associated with increment in the T allele number.
Conclusions
The presence of the eNOS 894T allele had a significantly negative impact on responsiveness to a selective α1-blocker in BPH/LUTS treatment, suggesting that eNOS G894T gene polymorphism may be a genetic susceptibility factor for α1-blocker efficacy in men with BPH/LUTS.