Editorial: Somatic-autonomic neurorrhaphy for erectile function restoration after radical prostatectomy
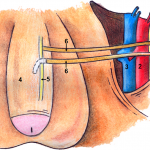
The authors of the present study [1] are to be commended for their efforts in describing their 3-year experience with a novel bilateral end-to-side somatic-autonomic neurorrhaphy intended to restore erectile function at least 24 months after radical prostatectomy, after which spontaneous return of erectile function is unlikely [2]. Using the principles of brain plasticity and neurotization, the authors describe, for the first time, bilateral sural neurografting between the femoral nerve and both the corpus cavernosum and the dorsal nerve of the penis to achieve penile re-innervation. The employed side-to-end neurorrhaphy theoretically limits functional damage during axonal sprouting, reinforces sensory–motor communications to the cavernous nerves, and promotes glans penis sensitivity, although direct evidence of these physiological and clinical outcomes is yet to be demonstrated. Furthermore, the authors astutely capitalize on the potential advantages of using a femoral donor nerve, including its proximity to the proximal penis, its diameter, the sufficient axon count, the mixed composition of sensory and motor fibres, and its secretion of acetylcholine which is an essential neurotransmitter in the nitric oxide-mediated pathway leading to penile tumescence.
What is especially singular about this technique is its application months after radical prostatectomy following demonstrated post-surgical loss of erectile function. Previous studies have focused on unilateral or bilateral sural [3-6] or genitofemoral [7] neurografting of the cavernous nerves at the time of radical prostatectomy before post-surgical loss of erectile function could be substantiated. Such studies have had mixed results, attributable in part to the success of the nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy technique in the hands of experienced high-volume surgeons [3, 6], and post-surgical exposure of the cavernous nerves to androgen deprivation or radiation therapy in some patients [3, 5]. Whereas post-radical prostatectomy re-innervation of the cavernous nerves may not be feasible or efficacious secondary to post-surgical and post-radiation fibrosis, the described technique does not require abdominopelvic access, is associated with a quick recovery time and minimal complications, and does not preclude subsequent penile prosthesis implantation if necessary.
The results of the present study show significant improvement in general sexual satisfaction from baseline to 6 months post intervention corresponding to achievement of flaccid erection for all patients; significant improvement in erectile dysfunction from baseline to 12 months post intervention corresponding to achievement of semi-rigid or rigid erections in 8/10 patients; and significant improvement in satisfaction with sexual intercourse from baseline to 18 months post intervention corresponding to achievement of penetration for 6/10 patients. It should be noted, however, that administration of the Clinical Evolution of Erectile Function instrument at 36 months postoperatively may have introduced recall bias in patient-reported erectile function. As would be expected, no significant differences were noted in sexual desire or orgasm satisfaction during the study period. These results were achieved without evidence of atrophy, fibrosis, or significant differences in vascular flow of the bilateral corpora cavernosa; and with minimal complications over the study period.
The present study provides preliminary data regarding the safety, feasibility and efficacy of bilateral sural neurografting between the femoral nerve and both the corpus cavernosum and the dorsal nerve of the penis to restore post-radical prostatectomy erectile function in a limited pool of 10 men. If these preliminary results are substantiated with long-term follow-up in a significant number of patients, it should prompt multi-institutional collaborations to appropriately power comparative effectiveness analyses of post-radical prostatectomy neurorrhaphy, such as the described technique to a regulatory-approved ethical sham intervention, vacuum assist device therapy, urethral suppository therapy, or intracavernosal injection therapy. Ideally, patients should be matched or statistical analyses should be controlled for patient age, relevant comorbidities, prostate cancer stage, pre-radical prostatectomy erectile function, nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy technique, androgen deprivation therapy, radiation therapy, response to phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition, and time interval between radical prostatectomy and intervention. Such multi-institutional studies would benefit from: standardized protocols for preoperative evaluation, operative technique, peri-operative care and post-surgical sexual stimulation; repeated-measure analyses of both objective assessments of the quality and duration of penile tumescence, as well as patient-reported outcomes of erectile function and disease-specific quality of life using validated instruments; report of oncological outcomes; and long-term follow-up. We would encourage the authors to produce a technical video demonstrating their technique so that it may be attempted and validated by other programmes. Urological surgeons with expertise in oncology, sexual function, and reconstruction may collaborate and pool patient data to achieve high-powered quality studies of novel techniques, such as the one described in the present study, for post-radical prostatectomy erectile function restoration.
How to Cite
Cavallo, J. A. and Tewari, A. K. (2017), Somatic-autonomic neurorrhaphy for erectile function restoration after radical prostatectomy. BJU International, 119: 816–818. doi: 10.1111/bju.13858
References