Editorial: Combining solifenacin and mirabegron for OAB management
Overactive bladder (OAB) is one of the most frequent LUTS in both sexes, and is associated with significant bother and impact on quality of life [1]. In many cases, no underlying cause is found and OAB is stated as being ‘idiopathic’. Until recently, the first-line management of idiopathic OAB has been based on the use of antimuscarinics, solifenacin being one of the most prescribed drugs; however, the long-term adherence to antimuscarinics has been shown to be rather low because of lack of efficacy, treatment switch or adverse events, or for mixed reasons [2].
A few years ago, β3-adrenergics were successfully introduced as an alternative to antimuscarinics for OAB management. The efficacy of β3-adrenergics has been shown and they are associated with a new safety profile that differs from that of antimuscarinics [3]. Mirabegron, the most widely used β3-adrenergic drug, has thus gained popularity in clinical practice. Given that β3-adrenergics and anticholinergics have a distinct mechanism of action, the combination of both drugs has been seen as a possible option and has been tested through a huge randomized controlled trial [4].
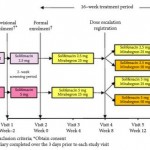
In the present issue of BJUI, Yamaguchi et al. [5] report the results of the MILAI study, an open-label phase IV trial assessing the effects of mirabegron as an add-on therapy in patients treated for OAB with solifenacin. They found that the addition of mirabegron to solifenacin generated only mild to moderate adverse events, and led to promising efficacy results; however, this study, which the authors call a preliminary study, raises a number of questions that remain completely unanswered.
First, even if seen as fluctuant, idiopathic OAB is considered to be a chronic disease. Long-term results must be seen as a critical issue in the field, and there is no guarantee that the short-term data presented in the MILAI study will stand the test of time in terms of efficacy and adherence.
Second, the study raises an important question about the optimum use of mirabegron in idiopathic OAB. Should it be a first-line option, a secondary option after antimuscarinics (available for treatment switch), or an add-on therapy, as it is presented in the present trial? There might be some room for each of these pathways depending on the patient history and characteristics, and the results obtained under antimuscarinics. From that point of view, the MILAI study is probably too weak to identify factors associated with failure of the combination therapy. Further studies should better detail patient inclusion criteria (because ‘failure’ of antimuscarinics is a heterogeneous concept), as well as characteristics of non-responders. In the present study, these two points are not detailed, and the study provides only a global statistically significant improvement, paving the way for additional research. A better understanding of the mechanism of action of the treatment combination would be of great value to move forward and enable better patient selection.
Finally, one of the upcoming challenges will be to integrate mirabegron as an add-on therapy in the world of male LUTS, including benign prostatic obstruction, where β3-adrenergics probably have an important role to play. As underlined by the authors, several studies are on the way, and their results (in a male population) are urgently awaited.
After having been successfully introduced in most countries in the western world, the new life of mirabegron has begun (including post-marketing studies, extensions of market authorizations, potentially new indications, combination therapy). The future will tell us whether this success story will continue.
2 Veenboer PW, Bosch JL. Long-term adherence to antimuscarinic therapy in everyday practice: a systematic review. J Urol 2014; 191: 1003–8