Editorial: Choline-PET/CT in relapsing prostate cancer patients
18F-choline positron emission tomography (PET)/C T has become a modern imaging technique in men with prostate cancer and biochemical relapse after local treatment with curative intent (radical prostatectomy, external beam/intensity-modulated radiation therapy, brachytherapy) in order to differentiate between local, locoregional and systemic relapse. Although 18F-choline PET/CT will probably be replaced by prostate-specific membrane antigen-PET/CT in the near future, the present paper by Rodada-Marina et al. [1] is important for daily routine because the authors attempt to define the current role of 18F-choline PET/CT in the diagnostic algorithm of men with relapsing PSA and to define specific patient cohorts in whom 18F-choline PET/CT might have a significant impact in the decision-making process regarding the most appropriate treatment.
Two issues are important to me when discussing the potential indication for performing new imaging studies in my patients with relapsing PSA: (1) whether the method is sensitive enough to detect a metastatic deposit at a given PSA serum concentration and (2) whether a positive finding using this imaging method would change my treatment recommendation. In this context, the current recommendation is 18F-choline PET/CT at a PSA serum concentration >1 ng/mL if a therapeutic consequence will be drawn [2]. If the patient would not be a candidate for a secondary local treatment option, such as salvage radiation therapy or salvage radical prostatectomy, but he would be treated with androgen deprivation therapy anyhow, none of the modern imaging studies would make sense.
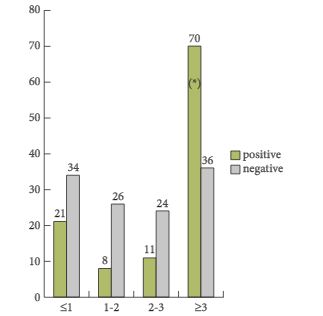
In the present paper, a total of 233 patients from six different institutions were included in a retrospective study. One of the most important findings of this paper is that the detection rate was only 47.6%, despite relatively high mean and median trigger PSA serum levels of 5.3 and 2.8 ng/mL, respectively. The detection rates varied between 23.5 and 38.2% in men with PSA serum levels between <1 and 2–3 ng/mL and the detection only increased to 67% in men with PSA levels ≥3 ng/mL. Moreover, the authors identified that the best threshold for the trigger PSA level was 3.5 ng/mL, with a sensitivity and a specificity of 64 and 76%, respectively. With regard to PSA doubling time (PSA-DT), the best threshold was < 6 months, with a sensitivity and a specificity of 58% only. Based on these very high PSA serum levels at the time of imaging studies, which had the potential intent to select the most appropriate therapy, the majority of patients were already beyond the scope of secondary local therapy with curative intent [2, 3]. Furthermore, it was shown that patients with a Gleason score 8–10 and a PSA-DT of <6 months have a higher probability of having systemic disease – a fact which is well known already.
What do these data mean for clinical practice? There might be three clinical scenarios in which imaging studies might exert a significant impact on further treatment: (1) salvage radiation therapy in men with PSA relapse after radical prostatectomy (RP) [2, 3], (2) salvage RP after radiation therapy of the prostate [4] and (3) salvage pelvic lymphadenectomy in men with PSA relapse after RP or radiation therapy of the prostate [5]. In my view, the data underline the fact that imaging with 18F-choline PET/CT is not helpful in the first clinical scenario, early or late PSA relapse after RP. The clinician needs to start local salvage therapy, such as percutaneous radiation therapy, at a serum PSA concentration well below 0.5 ng/mL if a curative intent is the focus of treatment [2, 3]. Based on the current data, only one fifth of the patient cohort had a positive 18F-choline PET/CT finding even when considering aggressive biological features such as a high Gleason score, a rapid PSA-DT and a high PSA nadir after RP; therefore, PET/CT does not add significant additional diagnostic information in the individual patient so that it does not appear useful to perform 18F-choline PET/CT in men with low PSA levels at time of relapse. 18F-choline PET/CT might be helpful in the second clinical scenario to identify patients who will benefit from salvage RP. It has been shown that a PSA < 10 ng/mL and a PSA-DT >12 months at time of surgery are the most significant prognosticators for identifying organ-confined disease [4]. A positive detection rate for metastatic foci would be >75% in this scenario, underlining the indication for performing choline PET/CT. With regard to the third clinical scenario, it has been shown that a serum PSA <4 ng/mL and a slow PSA-DT represent prognostic markers for selecting men who most probably have locoregional relapse in the small pelvis and who will benefit the most from salvage lymphadenectomy [5]. Again, choline-PET/CT is indicated to exclude retroperitoneal or systemic disease and it should be performed before any salvage procedure.
In conclusion, the retrospective study performed by Rodado-Marina et al. [1] provides significant and clinically useful information with regard to the definition of a patient cohort that would benefit most from the performance of a choline PET/CT. This information should be considered when counselling patients with regard to the need for new imaging methods at the time of PSA relapse.