Editorial: Can systematic biopsy be safely avoided at the time of MRI/ultrasonography fusion biopsy?
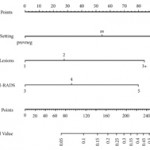
In clinical practice, the need for maximising prostate cancer detection is often balanced against the theoretical risks of infection, bleeding, and pain associated with taking additional cores. In this novel study, Sathianathen et al. [1] provide a tool for measuring the oncological benefit of including concurrent systematic biopsy (SB) at the time of MRI‐guided targeted biopsy (TB). There were several key findings: (i) Amongst patients undergoing MRI‐guided biopsy (all biopsy settings), 11.6% were found to have significant cancers detected by SB alone; (ii) Amongst patients who had clinically significant cancers detected by SB alone, 52.2% were sampled within sextants outside the targeted regions of interest; (iii) According to the proposed nomogram, patients with prior negative biopsies, fewer MRI lesions, and lower Prostate Imaging‐Reporting and Data System (PI‐RADS) scores were at the lowest risk of missing significant cancer when SB was omitted.
Based on the present study, biopsy setting appears to be a key factor for deciding whether to omit SB. In the subset of patients undergoing primary biopsy, the authors found that 18.5% of cancers were detected by SB alone. These results are consistent with those of the MRI‐FIRST trial, which showed 14% of cancers were detected by SB only, 20% by TB only, and 66% by combining both techniques [2]. MRI‐FIRST concluded that in the primary biopsy setting, there was no difference between SB and TB in detection of clinically significant prostate cancer, although combining both techniques provided the highest detection rate.
Prior negative biopsy cohorts are generally at lower risk of harbouring significant cancer, as many cancers have already been ‘selected out’ by initial biopsies. In this setting, TB plays an important role in sampling tumour foci in difficult‐to‐reach regions of the prostate (e.g., anterior and apical) [3]. According to the authors’ nomogram, prior negative biopsy patients were least likely to benefit from concurrent SB. While the authors suggest a paradigm of selectively omitting SB, some authors have proposed omitting both TB and SB altogether in select patients. A previously reported multi‐institutional nomogram can be used to predict benign pathology after MRI‐guided biopsy, which can help reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies after MRI in the prior negative biopsy setting [4]. This clinical tool was further externally validated and optimised by Bjurlin et al. [5].
The ‘active surveillance (AS)’ setting typically refers to a confirmatory MRI‐guided biopsy in men with Grade Group 1 prostate cancer prior to enrollment in AS. Recently, the presence of cribriform morphology in Grade Group 2 patients was confirmed to be a key poor prognostic feature that would exclude patients from AS [6]. The present study, however, did not account for different Gleason pattern 4 morphologies in their analysis, as ‘significant cancer’ was defined by Grade Group alone. Studies by independent groups have found that TB combined with SB was more accurate than either modality alone for detecting cribriform at the time of MRI‐guided biopsy [7, 8]. Therefore, concurrent SB is required to properly sample cribriform cancers in patients who are considering AS.
In this study, Sathianathen et al. [1] provide clinicians with a clinical tool for quantifying the added oncological value of concurrent SB. However, concurrent SB is probably prudent for most patients, particularly for those considering AS or focal therapy for which accurate determination of whole gland grade, cancer volume, and cribriform status are essential. As reducing the number of cores has not yet been shown to reduce biopsy‐related complications, are we willing to suboptimise cancer sampling without proven compensation?
by Matthew Truong
References
- , , et al. A clinical prediction tool to determine the need for concurrent systematic sampling at the time of magnetic resonance imaging‐guided biopsy. BJU 2019; 123: 612– 7
- , , et al. In patients with a previous negative prostate biopsy and a suspicious lesion on magnetic resonance imaging, is a 12‐core biopsy still necessary in addition to a targeted biopsy? BJU Int 2015; 115: 562– 70
- , , et al. Multi‐institutional nomogram predicting benign prostate pathology on magnetic resonance/ultrasound fusion biopsy in men with a prior negative 12‐core systematic biopsy. Cancer 2018; 124: 278– 85
- , , et al. Predicting benign prostate pathology on magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion biopsy in men with a prior negative 12‐core systematic biopsy: external validation of a prognostic nomogram. Eur Urol Focus 2018. [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2018.05.005
- , , et al. Presence of invasive cribriform or intraductal growth at biopsy outperforms percentage grade 4 in predicting outcome of Gleason score 3+4=7 prostate cancer. Mod Pathol 2017; 30: 1126– 32
- , , et al. A comprehensive analysis of cribriform morphology on magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion biopsy correlated with radical prostatectomy specimens. J Urol 2018; 199: 106– 13
- , , et al. Role of magnetic resonance imaging targeted biopsy in detection of prostate cancer harboring adverse pathological features of intraductal carcinoma and invasive cribriform carcinoma. J Urol 2018; 200: 104– 13