Article of the Week: Co-administration of TRPV4 and TRPV1 antagonists potentiate the effect of each drug
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Prof. Francisco Cruz, discussing his paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Co-administration of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) and TRPV1 antagonists potentiate the effect of each drug in a rat model of cystitis
Ana Charrua†‡§, Célia D. Cruz‡§, Dick Jansen¶ , Boy Rozenberg¶ , John Heesakkers¶ and Francisco Cruz*†§
*Department of Urology, S. João Hospital, †Department of Renal, Urologic and Infectious Disease, ‡Department of Experimental Biology, Faculty of Medicine of the University of Porto, §IBMC – Instituto de Biologia Molecular e Celular da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, and ¶Department of Urology, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
OBJECTIVE
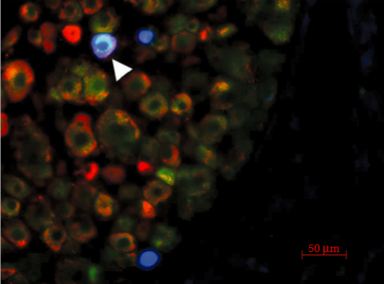
To investigate transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) expression in bladder afferents and study the effect of TRPV4 and TRPV1 antagonists, alone and in combination, in bladder hyperactivity and pain induced by cystitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
TRPV4 expression in bladder afferents was analysed by immunohistochemistry in L6 dorsal root ganglia (DRG), labelled by fluorogold injected in the urinary bladder. TRPV4 and TRPV1 co-expression was also investigated in L6 DRG neurones of control rats and in rats with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cystitis. The effect of TRPV4 antagonist RN1734 and TRPV1 antagonist SB366791 on bladder hyperactivity and pain induced by cystitis was assessed by cystometry and visceral pain behaviour tests, respectively.
RESULTS
TRPV4 is expressed in sensory neurones that innervate the urinary bladder. TRPV4-positive bladder afferents represent a different population than the TRPV1-expressing bladder afferents, as their co-localisation was minimal in control and inflamed rats. While low doses of RN1734 and SB366791 (176.7 ng/kg and 143.9 ng/kg, respectively) had no effect on bladder activity, the co-administration of the two totally reversed bladder hyperactivity induced by LPS. In these same doses, the antagonists partially reversed bladder pain behaviour induced by cystitis.
CONCLUSIONS
TRPV4 and TRPV1 are present in different bladder afferent populations. The synergistic activity of antagonists for these receptors in very low doses may offer the opportunity to treat lower urinary tract symptoms while minimising the potential side-effects of each drug.