Article of the Week: Patient expectations of sexual function following RP
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
A survey of patient expectations regarding sexual function following radical prostatectomy
Objective
To assess the understanding of patients, who had previously undergone radical prostatectomy (RP), about their postoperative sexual function, as clinical experience suggests that some RP patients have unrealistic expectations about their long-term sexual function.
Patients and Methods
Patients presenting within 3 months of their open RP or robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) were questioned about the sexual function information that they had received preoperatively. Patients were questioned about erectile function (EF), postoperative ejaculatory status, orgasm, and postoperative penile morphology changes. Statistical analyses were performed to assess for differences between patients who underwent open RP vs RALP.
Results
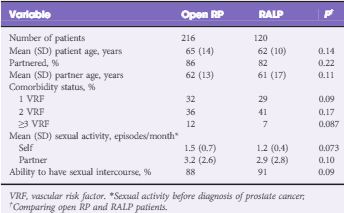
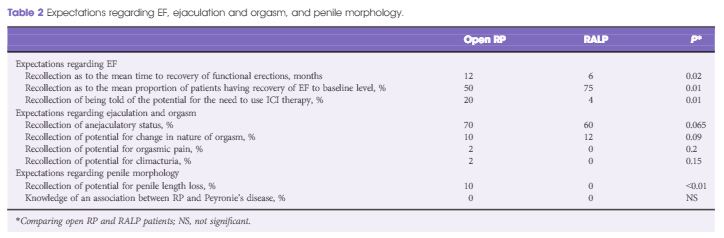
In all, 336 consecutive patients (from nine surgeons) with a mean (SD) age of 64 (11) years had the survey instrument administered (216 underwent open RP and 120 underwent RALP). There were no significant differences in patient age or comorbidity profiles between the two groups. Only 38% of men had an accurate recollection of their nerve-sparing status. The mean (SD) elapsed time after RP at the time of postoperative assessment was 3 (2) months. RALP patients expected a shorter EF recovery time (6 vs 12 months, P = 0.02), a higher likelihood of recovery back to baseline EF (75% vs 50%, P = 0.01), and a lower potential need for intracavernosal injection therapy (4% vs 20%, P = 0.01). Almost half of all patients were unaware that they were rendered anejaculatory by their surgery. None of the RALP patients and only 10% of open RP patients recalled being informed of the potential for penile length loss (P < 0.01) and none were aware of the association between RP and Peyronie’s disease.
Conclusions
Patients who have undergone RP have largely unrealistic expectations about their postoperative sexual function.