Article of the Week: Management and Outcomes of RMC
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video discussing the paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Management and outcomes of patients with renal medullary carcinoma: a multicentre collaborative study
Abstract
Objective
To describe the management strategies and outcomes of patients with renal medullary carcinoma (RMC) and characterise predictors of overall survival (OS).
Patients and Methods
RMC is a rare and aggressive malignancy that afflicts young patients with sickle cell trait; there are limited data on management to date. This is a study of patients with RMC who were treated in 2000–2015 at eight academic institutions in North America and France. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate OS, measured from initial RMC diagnosis to date of death. Cox regression analysis was used to determine predictors of OS.
Results
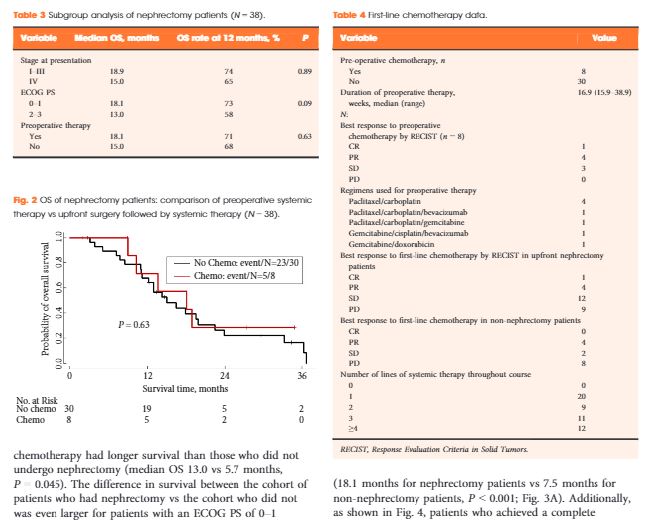
In all, 52 patients (37 males) were identified. The median (range) age at diagnosis was 28 (9–48) years and 49 patients (94%) had stage III/IV. The median OS for all patients was 13.0 months and 38 patients (75%) had nephrectomy. Patients who underwent nephrectomy had superior OS compared to patients who were treated with systemic therapy only (median OS 16.4 vs 7.0 months, P < 0.001). In all, 45 patients received chemotherapy and 13 (29%) had an objective response; 28 patients received targeted therapies, with 8-week median therapy duration and no objective responses. Only seven patients (13%) survived for >24 months.
Conclusions
RMC carries a poor prognosis. Chemotherapy provides palliation and remains the mainstay of therapy, but <20% of patients survive for >24 months, underscoring the need to develop more effective therapy for this rare tumour. In this study, nephrectomy was associated with improved OS.