Article of the Week: Assessing extranodal extension and the size of the largest lymph node metastasis after RP
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Prognosis of patients with pelvic lymph node metastasis following radical prostatectomy: value of extranodal extension and size of the largest lymph node metastasis
Niccolo M. Passoni, Harun Fajkovic*, Evanguelos Xylinas†, Luis Kluth‡, Christian Seitz*, Brian D. Robinson§, Morgan Rouprêt¶, Felix K. Chun‡, Yair Lotan**, Claus G. Roehrborn**, Joseph J. Crivelli§, Pierre I. Karakiewicz††, Douglas S. Scherr§, Michael Rink‡, Markus Graefen‡, Paul Schramek*, Alberto Briganti, Francesco Montorsi, Ashutosh Tewari§ and Shahrokh F. Shariat*§**
Department of Urology, Urological Research Institute, University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Italy, *Department of Urology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, †Department of Urology, Cochin Hospital, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, University Paris Descartes, ¶Academic Department of Urology of la Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Faculté de medicine Pierre et Marie Curie, University Paris VI, Paris, France, ‡Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf, Martini Clinic, Prostate Cancer Center at University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, §Department of Urology and Pathology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY, **Department of Urology, Southwestern Medical Center, University of Texas, Dallas, TX, USA, and ††Department of Urology, University of Montreal, Montreal, QC, Canada
OBJECTIVE
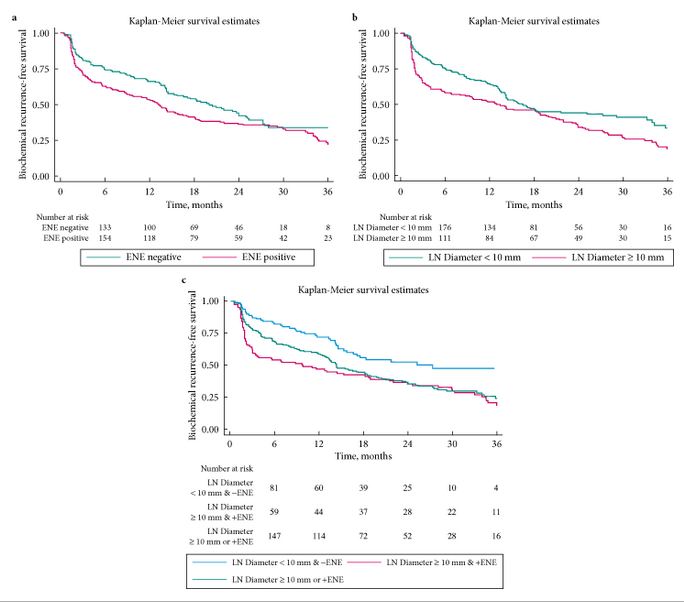
- To assess the prognostic role of extranodal extension (ENE) and the size of the largest lymph node (LN) metastasis in predicting early biochemical relapse (eBCR) in patients with LN metastasis after radical prostatectomy (RP).
PATIENTS AND METHODS
- We evaluated BCR-free survival in men with LN metastases after RP and pelvic LN dissection performed in six high-volume centres.
- Multivariable Cox regression tested the role of ENE and diameter of largest LN metastasis in predicting eBCR after adjusting for clinicopathological variables.
- We compared the discrimination of multivariable models including ENE, the size of largest LN metastasis and the number of positive LNs.
RESULTS
- Overall, 484 patients were included. The median (interquartile range, IQR) follow-up was 16.1 (6–27.5) months. The median (IQR) number of removed LNs was 10 (4–14), and the median (IQR) number of positive LNs was 1 (1–2).
- ENE was present in 280 (58%) patients, and 211 (44%) had their largest metastasis >10 mm. Patients with ENE and/or largest metastasis of >10 mm had significantly worse eBCR-free survival (all P < 0.01).
- On multivariable analysis, number of positive LNs (≤2 vs >2) and the diameter of LN metastasis (≤10 vs >10 mm), but not ENE, were significant predictors of eBCR (all P < 0.003).
- ENE and diameter of LN metastasis increased the area under the curve of a baseline multivariable model (0.663) by 0.016 points.
CONCLUSIONS
- The diameter of the largest LN metastasis and the number of positive LNs are independent predictors of eBCR.
- Considered together, ENE and the diameter of the largest LN metastasis have less discrimination than the number of positive LNs.