Article of the week: Persistent muscle-invasive BCa after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: an analysis of SEER‐Medicare data
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Persistent muscle‐invasive bladder cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: an analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results‐Medicare data
Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate whether patients with persistent muscle‐invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) after undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and radical cystectomy (RC) have worse overall survival (OS) and cancer‐specific survival (CSS) than patients with similar pathology who undergo RC alone.
Materials and Methods
Using the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER)‐Medicare database, we identified the records of patients with pT2‐4N0M0 disease who underwent RC, with and without NAC, for MIBC between 2004 and 2011. To evaluate survival outcomes in those with MIBC after NAC vs patients with MIBC who underwent RC alone, we used Kaplan–Meier time‐to‐event analysis and Cox proportional hazard regression modelling. Landmark analysis was conducted to mitigate immortal time bias. Propensity scoring was used to decrease the risk of selection bias.
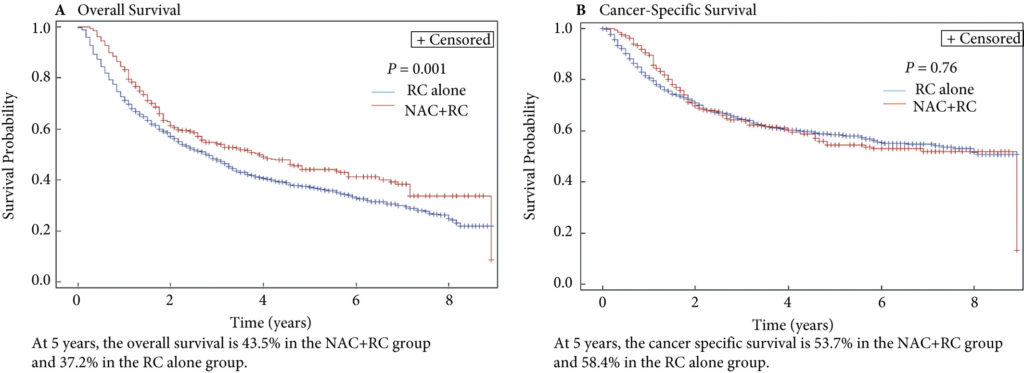
Fig. 2. Propensity‐weighted Kaplan–Meier curves. Overall survival and cancer‐specific survival among patients with persistent pT2‐4N0M0 bladder cancer after radical cystectomy from time of diagnosis. (A) Overall survival and (B) cancer‐specific survival. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) + radical cystectomy (RC) in red. RC alone in blue.
Results
Of the 1 886 patients with persistent pT2‐4 disease at the time of RC, 1505 underwent RC alone and 381 received NAC + RC. After adjusting for confounders, the propensity‐weighted risk of death from bladder cancer after diagnosis did not differ between the groups (hazard ratio [HR] 0.72, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.72–1.08; P = 0.23); however, the risk of death from all causes was worse in the RC‐alone group (HR 0.79, 95% CI0.67–0.94; P = 0.006).
Conclusions
Patients who had persistent MIBC after platinum‐based NAC + RC vs RC alone derived an OS benefit but not a CSS benefit from NAC. This may represent a selection bias favouring patients who were selected for NAC; however, the OS benefit was not evident in patients with persistent pT3‐T4N0M0 disease. This study underscores the importance of future research investigating methods to identify patients who will respond to NAC for bladder cancer. It also highlights the need to consider adjuvant therapy in patients who have persistent MIBC after NAC.