Article of the Week: Comparison of cSCI vs tSCI
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Comparison of spinal cord contusion and transection: functional and histological changes in the rat urinary bladder
Abstract
Objective
To compare the effect of complete transection (tSCI) and contusion spinal cord injury (cSCI) on bladder function and bladder wall structure in rats.
Materials and Methods
A total of 30 female Sprague–Dawley rats were randomly divided into three equal groups: an uninjured control, a cSCI and a tSCI group. The cSCI group underwent spinal cord contusion, while the tSCI group underwent complete spinal cord transection. At 6 weeks post-injury, 24-h metabolic cage measurement and conscious cystometry were performed.
Results
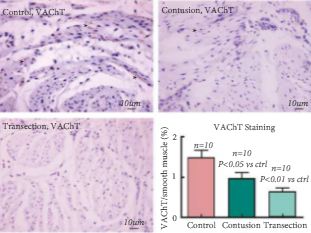
Conscious cystometry analysis showed that the cSCI and tSCI groups had significantly larger bladder capacities than the control group. The cSCI group had significantly more non-voiding detrusor contractions than the tSCI group. Both injury groups had more non-voiding contractions compared with the control group. The mean threshold pressure was significantly higher in the tSCI group than in the control and cSCI groups. The number of voids in the tSCI group was lower compared with the control group. Metabolic cage analysis showed that the tSCI group had larger maximum voiding volume as compared with the control and cSCI groups. Vesicular acetylcholine transporter/smooth muscle immunoreactivity was higher in the control than in the cSCI or tSCI rats. The area of calcitonin gene-related peptide staining was smaller in the tSCI group than in the control or cSCI groups.
Conclusions
Spinal cord transection and contusion produce different bladder phenotypes in rat models of SCI. Functional data suggest that the tSCI group has an obstructive high-pressure voiding pattern, while the cSCI group has more uninhibited detrusor contractions.




What is new in this study?