Editorial: The importance of knowing testosterone levels in patients with prostate cancer
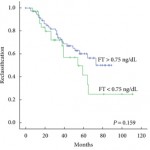
The paper by San Francisco et al. [1] in this issue of BJUI, reviews 154 patients with prostate cancer who were included in an active surveillance cohort. In all, 54 (35%) progressed to active treatment. Men who had disease reclassification had significantly lower free testosterone than those who were not reclassified. They concluded that on multivariate analysis, free testosterone and a family history of prostate cancer were independent predictors of disease reclassification. The authors acknowledge that this was a retrospective study of small size and the data was missing in some of the men, sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), luteinizing hormone and oestradiol were not measured. Nevertheless, this review adds to the increasing evidence that it is important to measure testosterone levels in men with prostate cancer.
Previous studies have indicated that a low testosterone level before treatment for prostate cancer is an independent predictor of a more aggressive high-grade cancer [2]. In addition to this, there appears to be an increased likelihood of extraprostatic disease at the time of diagnosis [3] and an unfavourable response to treatment [4].
Garcia-Cruz et al. [5] in 2012 reported that low testosterone bioavailability is related to a positive prostate cancer diagnosis in patients submitted for prostate biopsy. In a further study, he showed that low testosterone levels were related to poor prognosis factors in men with prostate cancer prior to treatment. Testosterone was inversely related to prostate cancer bilaterally and percentage of tumour in the biopsy. Higher testosterone levels were found in patients allocated to the low-risk progression group. In the multivariate analysis, older age and lower testosterone levels were related to a higher D’Amico risk of progression [5]. The researchers went on to show that higher SHBG and lower bioavailable testosterone are related to prostate cancer detection on biopsy. The study was a prospective analysis of 279 patients referred for prostate biopsy. Low bioavailable testosterone and high SHBG levels were related to a 4.9- and 3.2-fold increased risk of detection of prostate cancer on prostate biopsy taken due to an abnormal PSA result or an abnormal DRE [6].
Free testosterone accounts for about 1–2% of total testosterone and hence most circulating testosterone is bound to SHBG and as such, is inactive. Yamamoto et al. [7] had previously shown that men with a low free testosterone (<1.5 ng/dL) had an increased risk of a high Gleason score (>8) compared with men with higher free testosterone (8% vs 2%; P = 0.04). Additionally, a free testosterone level of <1.5 ng/dL was associated with increased risk of biochemical recurrence of tumour.
Morgentaler et al. [8] have been turning conventional wisdom upside down. They report on 13 symptomatic testosterone deficient men who also had untreated prostate cancer. The men received testosterone therapy while undergoing active surveillance for a median of 2.5 years. None of the men had aggressive or advanced prostate cancer and they were rigorously followed up. Despite effective treatment, neither the PSA level nor prostate volume showed any change. Follow-up biopsies were taken in all of the men at yearly intervals and none developed cancer progression.
It is intriguing to think that the decline in testosterone with age and comorbidities may contribute to tumorigenesis in the prostate. Clearly this study needs to be replicated with much larger numbers. But it seems reasonable to suggest that we ought to know about the hormonal environment existing in our patients with prostate cancer. This will of course, raise the even more controversial area of what to do about men with symptomatic hypogonadism with treated and untreated prostate cancer. There is limited data available on this issue.
Before considering testosterone therapy, the first step should be intensive lifestyle intervention; this is not only known to improve cancer survival, but raises total and free testosterone. Weight loss inhibits aromatase, and other complex cytokines, this reduces the suppression of the pituitary gonadal axis and conversion of testosterone to oestrogen, raising testosterone levels.
Michael Kirby*,†
*The Prostate Centre, London, and †Institute of Diabetes for Older People (IDOP), Beds & Herts Postgraduate Medical School, Puckeridge Bury Campus, Luton, UK
References
- San Francisco I, Rojas P, Dewolf W, Morgentaler A. Low free testosterone predicts disease reclassification in men with prostate cancer undergoing active surveillance. BJU Int 2014; 114: 229–235
- Massengill JC, Sun L, Moul JW et al. Pretreatment total testosterone level predicts pathological stage in patients with localized prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. J Urol 2003; 169: 1670–1675
- Chen SS, Chen KK, Lin AT, Chang YH, Wu HH, Chang LS. The correlation between pretreatment serum hormone levels and treatment outcome for patients with prostatic cancer and bony metastasis. BJU Int 2002; 89: 710–713
- Ribeiro M, Ruff P, Falkson G. Low serum testosterone and a younger age predict for a poor outcome in metastatic prostate cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 1997; 20: 605–608
- Garcia-Cruz E, Piqueras M, Huguet J et al. Low testosterone levels are related to poor prognosis factors in men with prostate cancer prior to treatment. BJU Int 2012; 110: E541–546
- Garcia-Cruz E, Carrión Puig A, Garcia-Larrosa A et al. Higher sex hormone-binding globulin and lower bioavailable testosterone. Scand J Urol 2013; 47: 282–289
- Yamamoto S, Yonese J, Kawakame S et al. Preoperative serum testosterone level as an independent predictor of treatment failure following radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2007; 52: 696–701
- Morgentaler A, Liphultz LI, Bennett R, Sweeney M, Avila D Jr, Khera M. Testosterone therapy in men with untreated prostate cancer. J Urol 2011; 185: 1256–1260