This blog was first posted at https://www.symplur.com/blog/the-urology-tag-ontology-project/
Urologists have been on the forefront of harnessing Social Media for professional use. Urological Organizations and Journals have used Social Media to lower barriers for information dissemination [1,2] [3] [4]. Meanwhile, Social Media engagement at Urological meetings has been used to augment the experience of attendees and allow remote “attendance” for those not able to physically be present at the meetings [5,6] [7]. Academic exchange through a formal Twitter-based Journal Club on the #urojc hashtag has enjoyed international participation [8]. Social Media has also been employed to assess the Media’s and the Public’s responses to news events in the Urologic clinical space [9], and guidelines for responsible and effective Social Media use now have been developed [10] [11]. Moreover, an extremely active patient advocacy voice has been growing louder on a number of the Social Media channels.
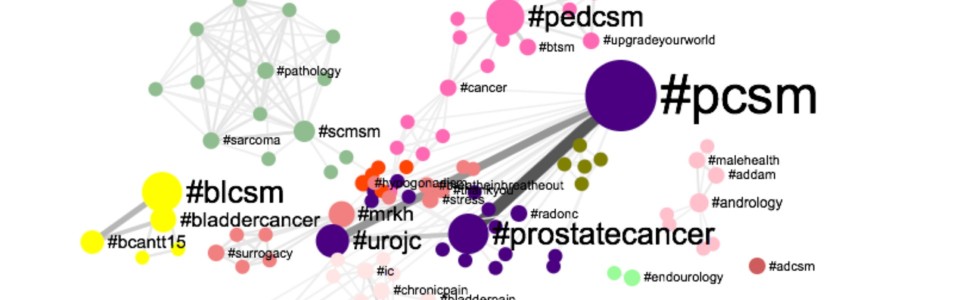
The Urology Tag Ontology Project aims to align hashtag use for this burgeoning Urological Social Media community. Utilizing this standardized list of Social Media communication descriptors, the project hopes to facilitate communication and promote collaboration in the healthcare provider and patient communities.
In creating the list, we crowd-sourced the Urologic Social Media community at large and were fortunate to receive buy-in from key stakeholders (Table 1).
Effective and standardized hashtag use remains an organic process that clearly cannot be dictated by a simple creation of a list. Indeed, the current list attempts to strike a balance between existing hashtags that enjoy heavy use and those descriptors that key opinion leaders in a particular urologic sub-specialty would like to see gain traction. As such, we hope for the Urology Tag Ontology Project to remain a “living document,” which is reassessed and updated on a regular basis.
Alexander Kutikov, MD, FACS @uretericbud
Associate Professor of Urologic Oncology
Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, USA @FoxChaseCancer
Associate Editor for Digital Media
European Urology @EUPlatinum
Henry Woo, MD @DrHWoo
Associate Professor of Surgery
University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Founder and Manager
International Urology Journal Club #urojc @iurojc
James Catto MB, ChB, PhD, FRCS @JimCatto
Professor in Urological Surgery
University of Sheffield
Editor-in-Chief
European Urology @EUPlatinum
Table 1: Urological Social Media Stakeholders Supporting Urology Tag Ontology Project
References
[1] Loeb S, Catto J, Kutikov A. Social media offers unprecedented opportunities for vibrant exchange of professional ideas across continents. European Urology 2014;66:118–9. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.048.
[2] Cress PE. Using Altmetrics and Social Media to Supplement Impact Factor: Maximizing Your Article’s Academic and Societal Impact. Aesthetic Surgery Journal 2014;34:1123–6. doi:10.1177/1090820X14542973.
[3] Nason GJ, O’Kelly F, Kelly ME, Phelan N, Manecksha RP, Lawrentschuk N, et al. The emerging use of Twitter by urological journals. BJU Int 2014:n/a–n/a. doi:10.1111/bju.12840.
[4] Loeb S, Bayne CE, Frey C, Davies BJ, Averch TD, Woo HH, et al. Use of social media in urology: data from the American Urological Association (AUA). BJU Int 2014;113:993–8. doi:10.1111/bju.12586.
[5] Matta R, Doiron C, Leveridge MJ. The dramatic increase in social media in urology. The Journal of Urology 2014;192:494–8. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2014.02.043.
[6] Canvasser NE, Ramo C, Morgan TM, Zheng K, Hollenbeck BK, Ghani KR. The Use Of Social Media in Endourology: An Analysis of the 2013 World Congress of Endourology Meeting. J Endourol 2014:140715142757008. doi:10.1089/end.2014.0329.
[7] Wilkinson SE, Basto MY, Perovic G, Lawrentschuk N, Murphy DG. The social media revolution is changing the conference experience: analytics and trends from eight international meetings. BJU Int 2015;115:839–46. doi:10.1111/bju.12910.
[8] Thangasamy IA, Leveridge M, Davies BJ, Finelli A, Stork B, Woo HH. International Urology Journal Club via Twitter: 12-Month Experience. European Urology 2014;66:112–7. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.01.034.
[9] Prabhu V, Lee T, Loeb S, Holmes JH, Gold HT, Lepor H, et al. Twitter Response to the United States Preventive Services Task Force Recommendations against Screening with Prostate Specific Antigen. BJU Int 2014;116:65–71. doi:10.1111/bju.12748.
[10] Rouprêt M, Morgan TM, Bostrom PJ, Cooperberg MR, Kutikov A, Linton KD, et al. European Association of Urology (@Uroweb) recommendations on the appropriate use of social media. European Urology 2014;66:628–32. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.06.046.
[11] Murphy DG, Loeb S, Basto MY, Challacombe B, Trinh Q-D, Leveridge M, et al. Engaging responsibly with social media: the BJUI guidelines. BJU Int 2014;114:9–11. doi:10.1111/bju.12788.